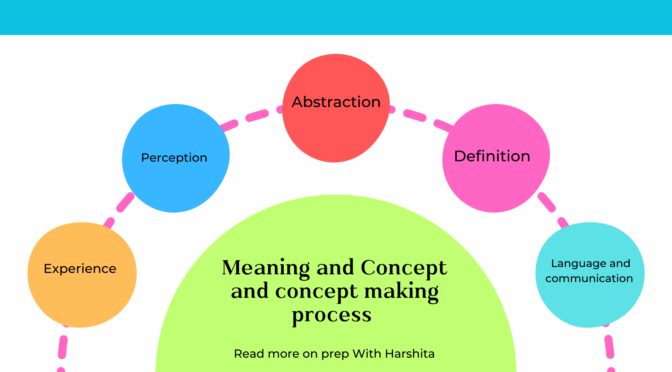
Discipline, in the context of academic study, refers to a branch of knowledge or a field of study that is characterized by a specific focus, methodology, and set of principles. It provides a framework for organizing and understanding information, and it often involves a systematic approach to acquiring knowledge. Disciplines are typically organized into subjects, which are more specific areas of study within a broader discipline.
Concept of Discipline :
Discipline consists of the rules, methods, and principles that define a particular field of study. It represents a way of organizing and categorizing knowledge to facilitate understanding and exploration within a specific domain. Disciplines often have their own unique terminology, theories, and methodologies.
Meaning of Discipline :
The meaning of discipline in the academic context is closely related to a particular branch of knowledge or an organized field of study. It involves following a set of rules, principles, and methods that guide research, learning, and practice within that field. For example, physics, psychology, and sociology are all disciplines that focus on specific aspects of the world.
Definition of Discipline:
Discipline can be defined as a branch of knowledge that is formally taught, researched, and practiced. It is characterized by its own set of theories, methods, and standards. Disciplines provide a structured framework for understanding and addressing specific phenomena or questions. For instance, biology is the discipline that studies living organisms and their interactions.
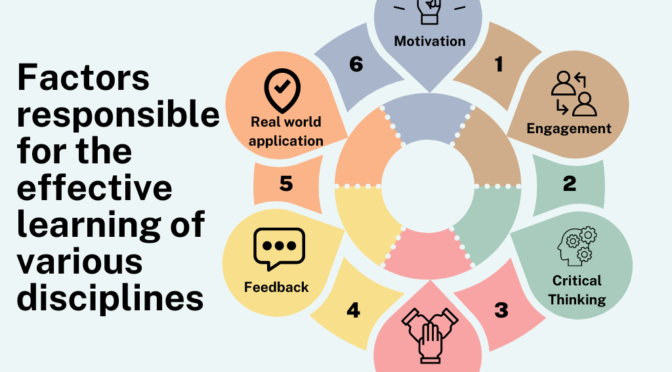
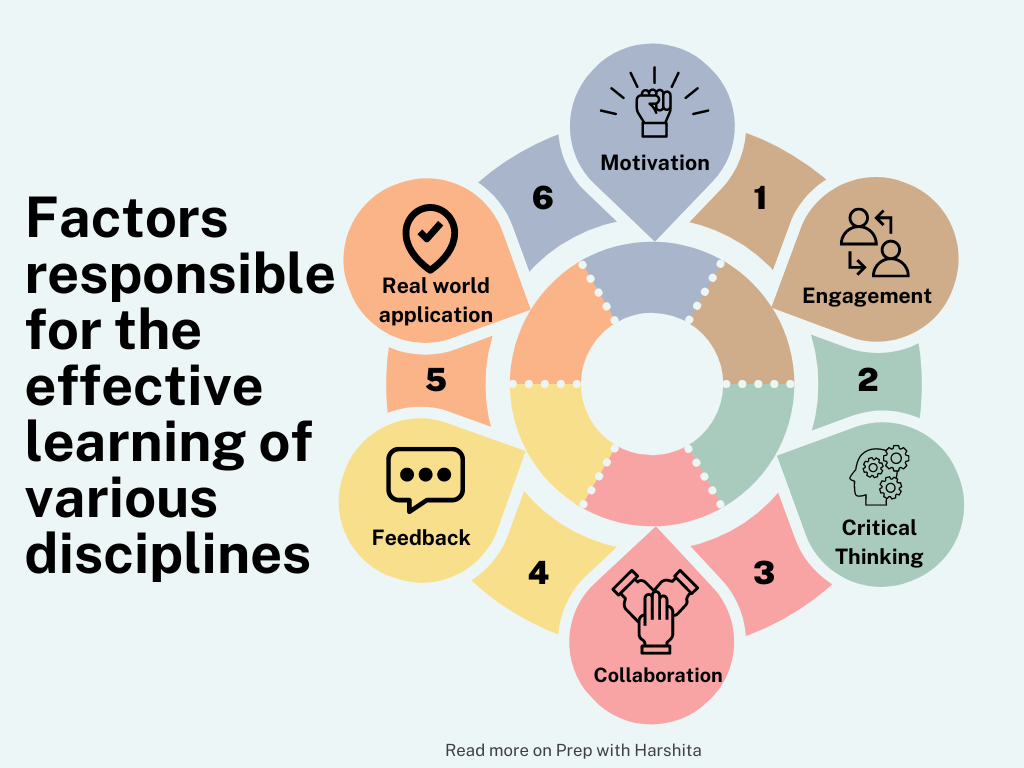
Characteristics of Discipline in Subject Understanding:
Specialization: Disciplines often involve specialization in a specific area of knowledge. For example, within the broader discipline of science, there are specialized fields like physics, chemistry, and biology.
Methodology: Each discipline has its own methodologies for conducting research and inquiry. The methods used in physics, for instance, differ from those used in history or psychology.
Terminology: Disciplines have their own unique vocabulary and terminology. This specialized language helps scholars communicate effectively within their field.
Foundational Theories: Disciplines are built upon foundational theories or principles that provide a basic understanding of that field.
Standards and Ethics: Disciplines often have established standards and ethical guidelines that researchers and practitioners are expected to follow. These standards contribute to the credibility and reliability of the discipline.
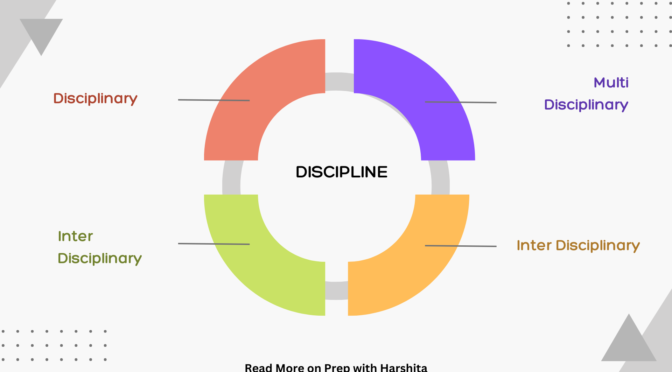
Interdisciplinary Connections: While disciplines are distinct, there are often interdisciplinary connections, where knowledge from one discipline can inform or enhance understanding in another.
Also Read: Understanding Discipline and Subjects

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita