Cognitive processes refer to the mental activities that enable us to acquire, process, and store information. Here are some of the types of cognitive processes:
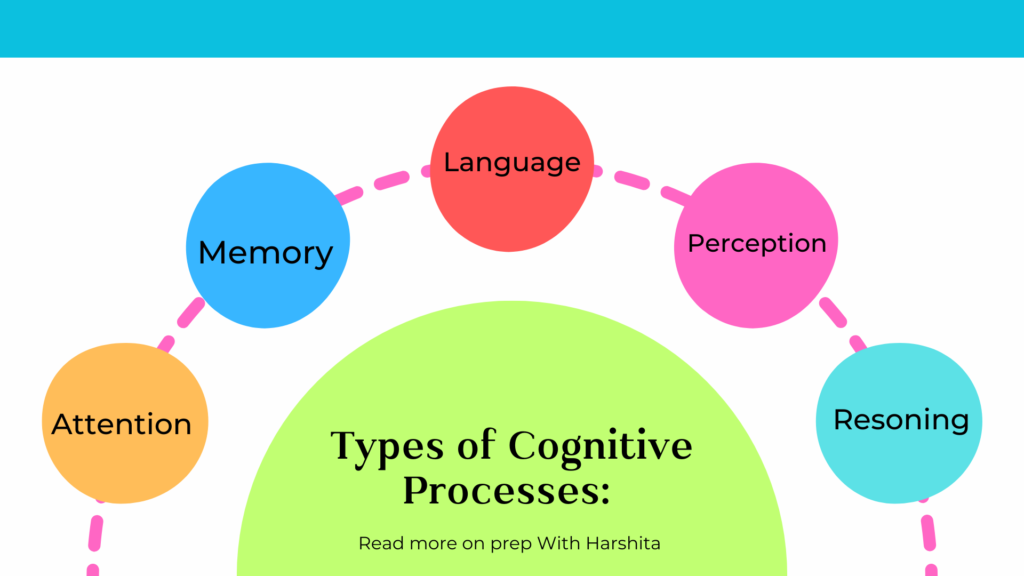
- Perception: Perception is the process of interpreting sensory information from the environment. It involves taking in information through the senses and organizing it into meaningful patterns.
- Attention: Attention is the ability to focus on specific information while ignoring distractions. It is a selective process that allows us to allocate our cognitive resources to the most important information.
- Memory: Memory is the process of encoding, storing, and retrieving information. It involves three stages: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
- Language: Language is a complex cognitive process that involves the acquisition and use of symbols, such as words and grammar, to communicate meaning.
- Reasoning: Reasoning is the process of using logic to draw conclusions from available information. It involves making deductions, inferences, and judgments.
- Problem-solving: Problem-solving is the process of finding a solution to a problem. It involves identifying the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating those solutions, and selecting the best one.
- Decision-making: Decision-making is the process of choosing between different options. It involves evaluating the pros and cons of each option and selecting the best one based on personal preferences and goals.
These cognitive processes work together to enable us to process and understand the world around us, and to make decisions and solve problems.
Also Read : Freud Psychoanalytical Theory
Also Read : Prep with Harshita