While group guidance can be an effective way to provide support and information to individuals, it also comes with certain disadvantages.
Here are some disadvantages of group guidance:
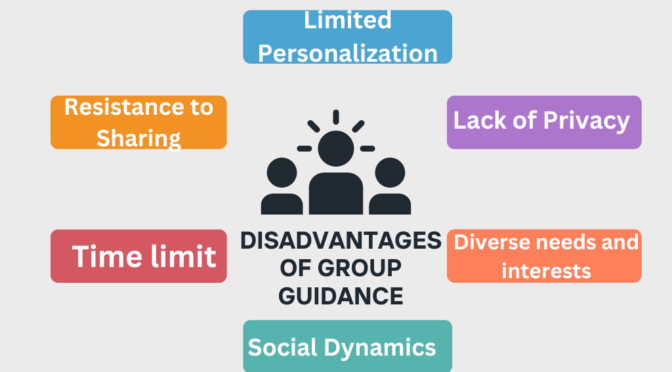
- Limited Personalization– Group guidance sessions may not address the specific needs or concerns of each individual in the group. The advice given may be generalized and may not be according to individual circumstances.
- Lack of Privacy– Group settings may not provide a confidential and private environment. Some individuals may be hesitant to share personal information or concerns in a group setting due to the fear of judgment or lack of privacy.
- Diverse needs and interests-Group members may have diverse needs, interests, and concerns. It can be challenging for a group facilitator to address the unique requirements of each participant, leading to some individuals feeling overlooked or not fully understood.
- Social dynamics– Group dynamics can impact the process of group guidance. Some individuals may be more dominant or outspoken, while others may be more reserved. This can create an uneven distribution of attention and support within the group.
- Time limit-In a group setting, there may be time constraints that limit the depth of discussion or discussion of individual concerns. Some participants may feel rushed or unable to fully express themselves within the allotted time.
- Resistance to sharing– Some individuals may be reluctant to share personal issues or concerns in a group, particularly if they are uncomfortable with public disclosure or if the issues are highly sensitive. This can limit the effectiveness of the guidance provided
- Homogeneity of information -In a group setting information may be presented in a standardized way to cater to the general audience. This may result in a lack of depth or specificity in addressing individual needs.
Also Read: Functions of a Counselor

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita