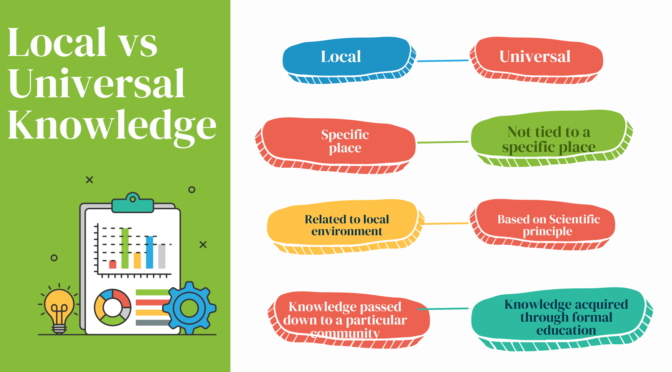
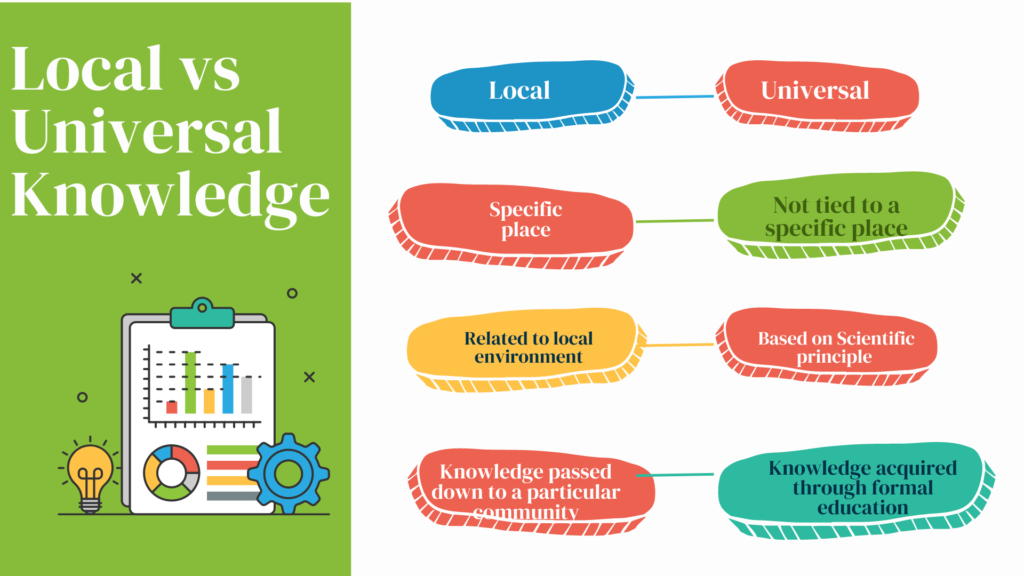
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique that involves producing a large number of ideas in a short period of time. The goal of brainstorming is to generate as many ideas as possible.
Osborn’s (1957) brainstorming is a group approach to encourage
creativity. It is a technique where people in a group setting are required to come up with as many ideas as possible. People or individuals give out whatever comes to their mind on a particular topic/issue without much thinking about it or postponing it or judging it. There are four basic guidelines for the group:
Features of Brain Storming Method :
(1) The greater the number of ideas, the better it is.
(2) People can combine two or more ideas that are proposed by others.
(3)The brainstorming session maintains the encouragement of each other, complete friendliness, and a relaxed mind.
(4) Group Involvement helps in the exchange of ideas and building a better communication system.
(5) People are not allowed to judge or criticize each other ideas so it is a good way to give ideas without being criticized.
(6) Participants are encouraged to think outside the box, be imaginative, and build on each other’s ideas.
Also Read: Assessment Techniques of Personality
These are some of the main features of brainstorming, which are effective in promoting creativity, generating new and innovative ideas, and solving problems in a group setting.