Teachers play a crucial role in identifying students’ attitudes, aptitudes, and interests at various school levels. Recognizing and understanding these aspects of students’ personalities can help educators tailor their teaching methods, provide individualized support, and guide students toward academic and career paths that align with their strengths and interests.
Here’s an overview of the role teachers play at different school levels:
Early Childhood Education (Preschool and Kindergarten):
Observation and Informal Assessment:
- Role: Teachers observe students during play, group activities, and interactions to identify early signs of interests and preferences.
- Method: Informal assessments, conversations, and play-based activities help in understanding children’s inclinations.
Encouraging Exploration:
- Role: Teachers create a rich and varied environment that allows children to explore different activities.
- Method: Offering a range of age-appropriate toys, books, and activities to stimulate curiosity and identify early interests.
Elementary School:
Individualized Conversations:
- Role: Teachers engage in one-on-one conversations to understand students’ likes, dislikes, and what excites them.
- Method: Personalized discussions during conferences or informal settings help reveal attitudes and interests.
Project-Based Learning:
- Role: Teachers design projects that allow students to explore topics in depth, helping to identify aptitudes and interests.
- Method: Project-based assessments and activities reveal areas where students demonstrate enthusiasm and proficiency.
Middle School:
Subject Exploration:
- Role: Teachers expose students to a variety of subjects, encouraging them to discover areas of interest and potential aptitude.
- Method: Rotational classes or exploratory courses help students sample different subjects.
Career Exploration Activities:
- Role: Teachers integrate career exploration activities to help students identify potential interests and align them with academic and career paths.
- Method: Guest speakers, field trips, and career-focused projects provide exposure to various professions.
High School:
Individualized Counseling:
- Role: Teachers act as advisors, guiding students through subject choices and career options based on their interests and aptitudes.
- Method: Career counseling sessions, aptitude tests, and personalized academic planning help in decision-making.
Incorporating Real-World Applications:
- Role: Teachers integrate real-world applications of academic concepts to demonstrate the relevance of learning.
- Method: Connecting classroom content to practical examples in various fields helps students see the applicability of their studies.
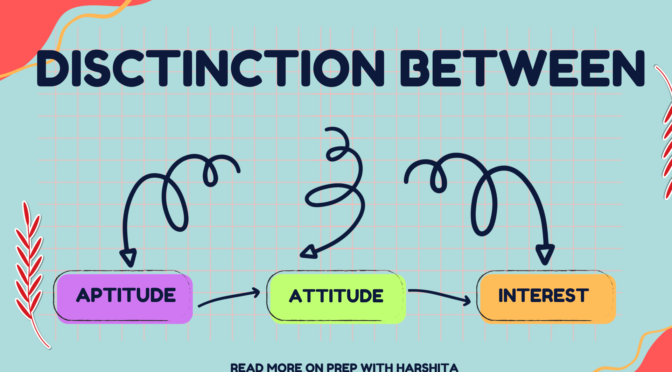
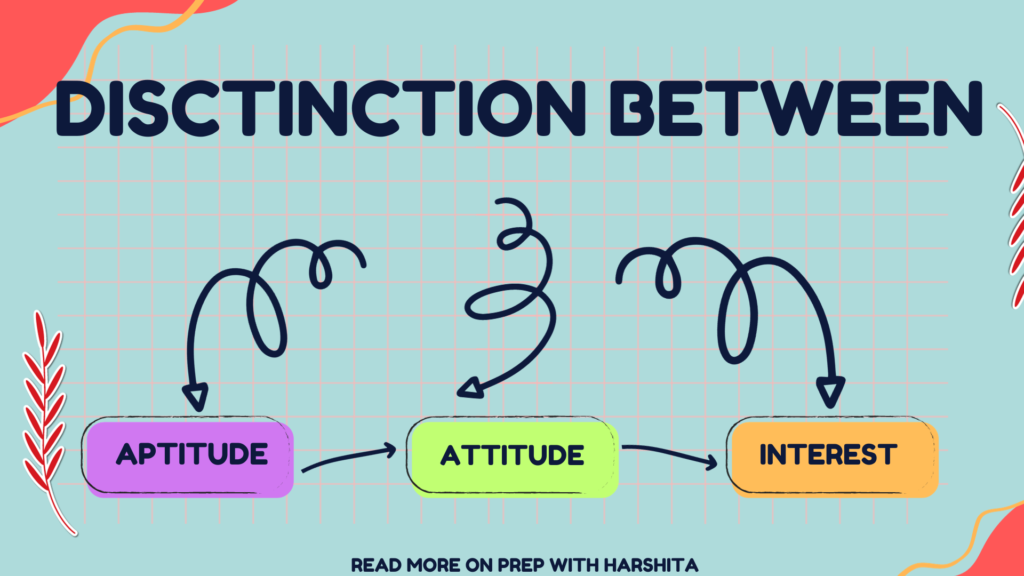
Also Read : Distinction among attitude aptitude intelligence

Also Visit : Prep with Harshita