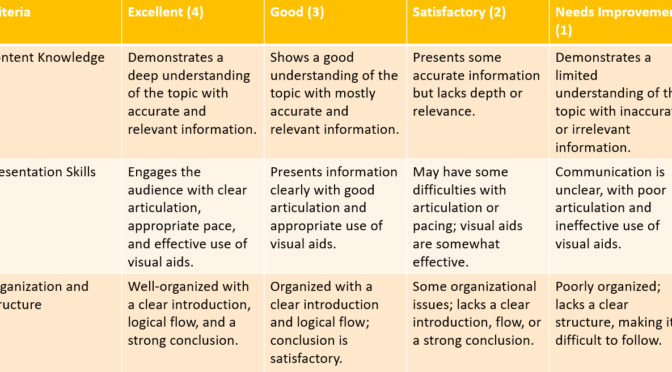
A rubric is a powerful tool for implementing a constructive approach to assessment. It provides a clear and detailed framework for evaluating students’ work based on specific criteria and learning objectives. Rubrics are commonly used in education at all levels, from primary school through higher education, and they can be applied to various types of assignments, projects, presentations, or assessments.
Key components of a rubric include:
Criteria: The specific aspects or dimensions of the assignment that will be evaluated. Criteria are often broken down into categories relevant to the learning objectives of the task.
Levels of Performance: Different levels or degrees of achievement for each criterion are defined. These levels typically range from high to low, indicating various degrees of proficiency or success.
Read more on the next page.
Also Read: Assessment as Learning