Motivation refers to the internal or external factors that drive a person to take action toward achieving a goal or fulfilling a need. It is the force that propels an individual to act, whether it is to complete a task, pursue a goal, or engage in a behavior.
Motivation is an important aspect of human behavior as it determines the level of effort, persistence, and determination a person will put into achieving a goal. It is also essential for personal and professional growth, as it helps individuals overcome challenges, adapt to changes, and achieve their full potential.
Also Read: Motivation Cycle
Types of Motivation :
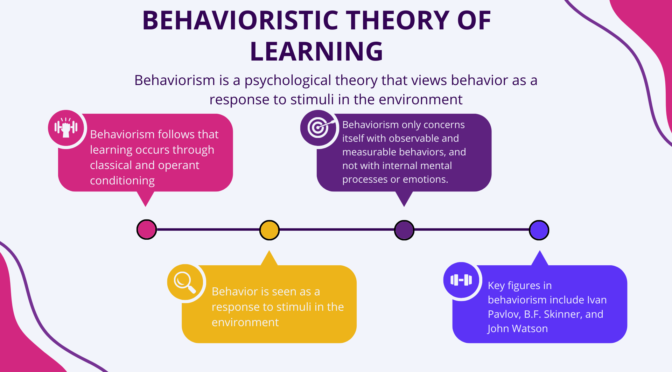
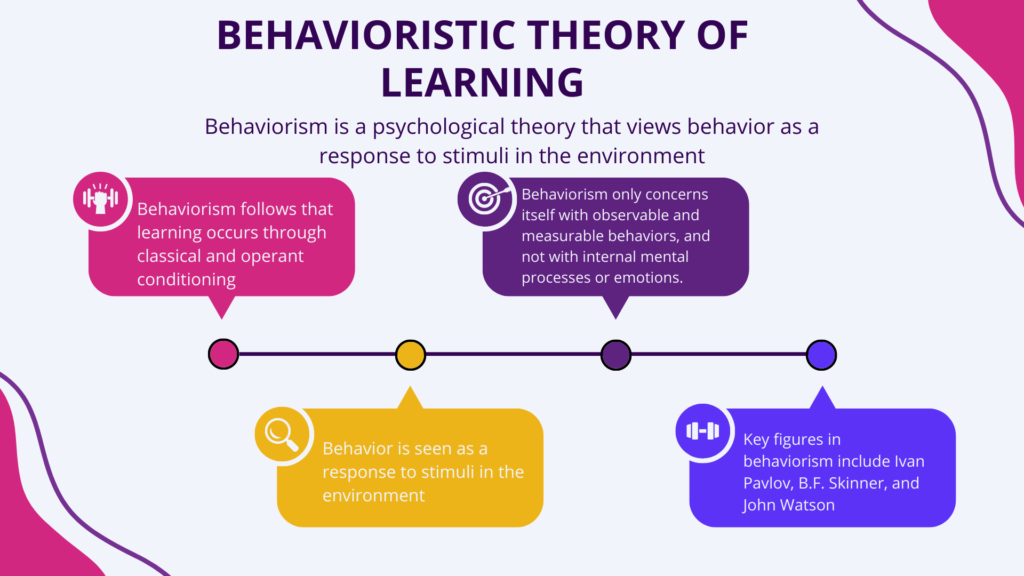
- Intrinsic motivation: It is the type of motivation that comes from within oneself. It is driven by personal satisfaction, interest, and enjoyment. Examples include pursuing a hobby, learning a new skill for personal growth, or doing something simply because it is enjoyable.
- Examples of intrinsic motivation include pursuing a hobby, learning a new skill , or doing something simply because it is enjoyable. Intrinsic motivation is often associated with positive emotions and a sense of personal fulfillment and satisfaction.
- Intrinsic motivation is generally more effective in promoting long-term behavior change and personal growth compared to extrinsic motivation. When individuals are intrinsically motivated, they are more likely to persist in their efforts. They become creative and innovative in finding solutions to problems.
- Extrinsic motivation: This type of motivation comes from external factors like rewards, recognition, or consequences. It is driven by external factors and not by personal satisfaction or interest. Examples include working for a salary, studying for good grades, or doing a task to avoid punishment.
- Examples of extrinsic motivation include working for a salary, studying for good grades, or doing a task to avoid punishment. Extrinsic motivation is related to external pressure or expectations, and may not necessarily reflect an individual’s personal interests or desires.
- Extrinsic motivation may be effective in promoting short-term behavior change but causes decreased motivation over time if the external rewards are removed. Individuals may become less interested in the activity or goal once the external reward is no longer available.