The Evolution of the National Education Policy of Education (NPE) is long one.
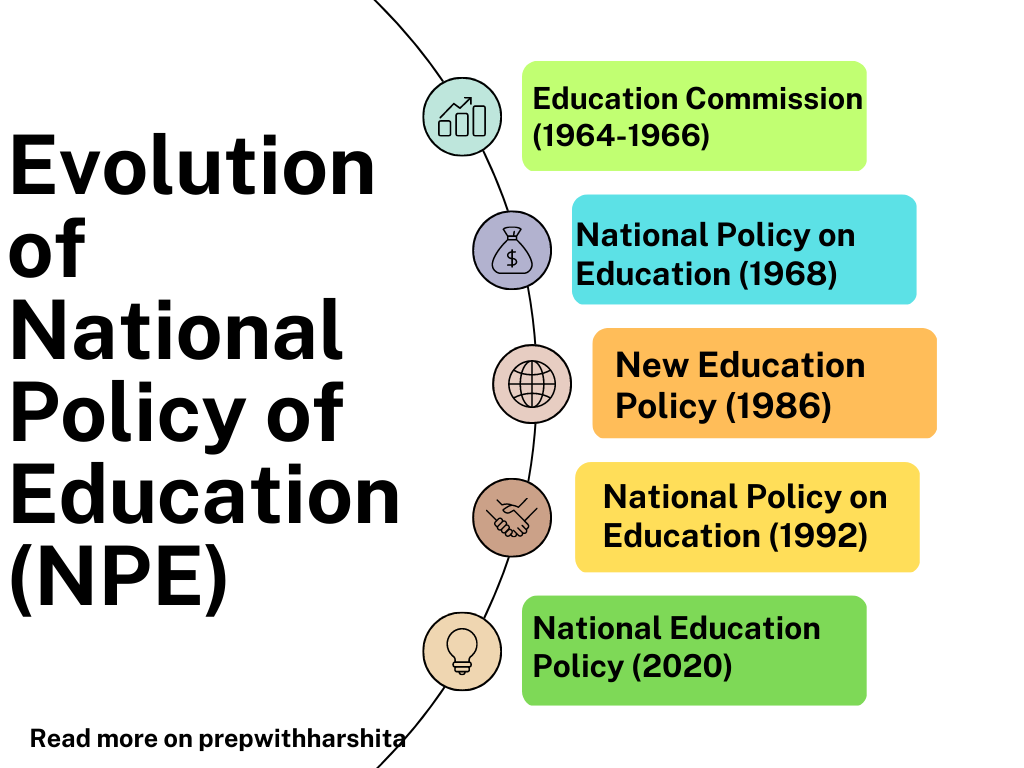
Stages of Evolution of National Education Policy (NPE)
The National Education Policy (NEP) in India has undergone several changes and reforms since the country’s independence in 1947.
Here is a brief overview of the evolution of the National Education Policy in India:
- First Five-Year Plan (1951-1956): The first National Education Policy was formulated during the first Five-Year Plan in 1952. The policy emphasized the importance of education in national development and focused on expanding access to education and improving the quality of education in the country.
- Second Five-Year Plan (1956-1961): The second National Education Policy was formulated during the second Five-Year Plan in 1960. The policy emphasized the need for a unified national education system and recommended the establishment of a national system of education with a common curriculum and examination system.
- Education Commission (1964-1966): The Education Commission, also known as the Kothari Commission, was established in 1964 to review the progress of education in India and make recommendations for the future. The Commission’s report, published in 1966, recommended a national system of education with a common structure and curriculum and emphasized the importance of vocational education and teacher training.
- National Policy on Education (1968): The National Policy on Education was formulated in 1968 based on the recommendations of the Kothari Commission. The policy emphasized the need for a unified national education system with a common structure and curriculum and emphasized the importance of vocational education, teacher training, and adult education.
- New Education Policy (1986): The New Education Policy was formulated in 1986, replacing the National Policy on Education of 1968. The policy focuses on the need for a child-centered and activity-based approach to learning. It also recommends the establishment of a three-tier system of education (elementary, secondary, and higher education).
- National Policy on Education (1992): The NPE was revised in 1992 to reflect the changing needs of society. The policy emphasized the need for a flexible and diversified education system. It recommended the establishment of a national system of vocational education and training.
- National Education Policy (2020): The latest National Education Policy was formulated in 2020 after a gap of almost three decades. The policy emphasizes the need for a holistic and multidisciplinary approach to learning. It also recommends the establishment of a four-tier system of education (Foundational, Preparatory, Middle, and Secondary). The policy also recommends reforms in teacher education, curriculum development, and assessment practices, among other things.
Overall, the evolution of the National Education Policy in India reflects the changing needs of society and the economy.
Also Read: PWD Act 1995