Values are beliefs or principles that guide our behavior and decision-making. Concept of Values and value education is deeply ingrained and learned through our culture, family, religion, and personal experiences. Values can be positive, such as honesty, respect, empathy, and responsibility, or negative, such as greed, selfishness, and intolerance.
What is Value Education?
- Value education is the process of teaching and instilling positive values and character traits in individuals. It involves the systematic development of a person’s ethical, moral, and social values through various educational strategies.
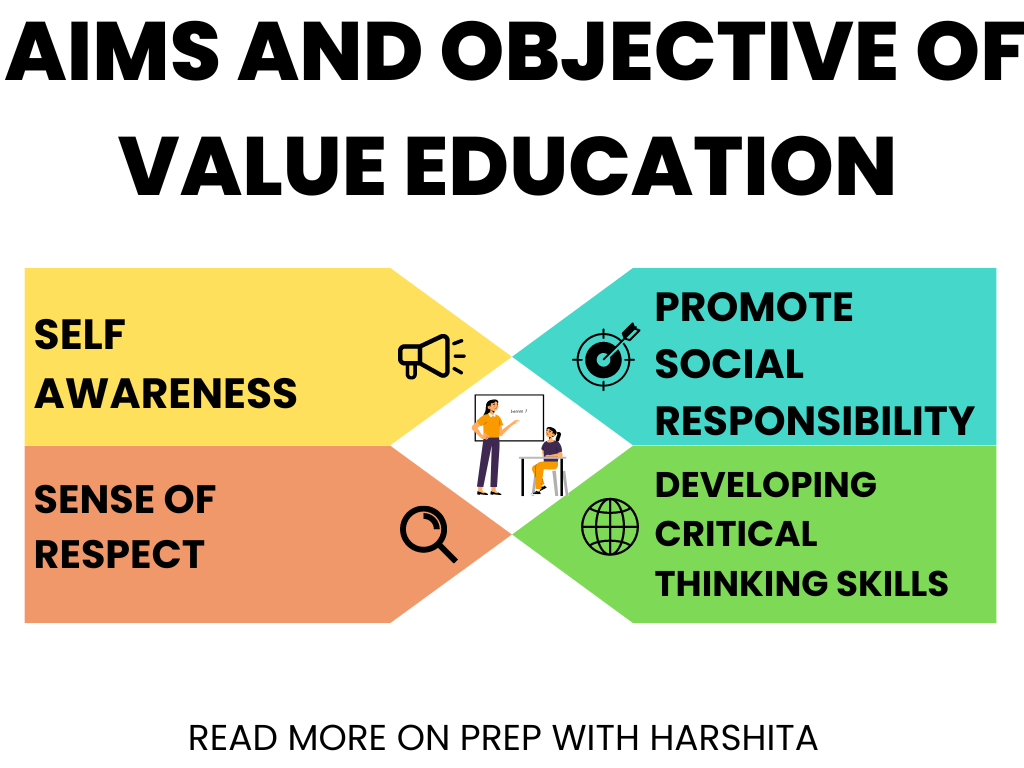
- The objective of value education is to promote positive behavior, attitudes, and ethics in individuals, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives and contribute positively to society.
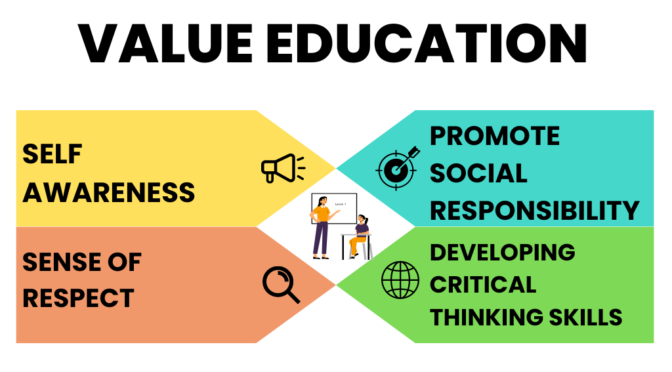
- Value education is important because it helps individuals to develop a strong sense of ethics and responsibility, which are essential for leading a successful and meaningful life. It also helps to promote social cohesion and a sense of community, by instilling values of respect, tolerance, and empathy.
- Value education also helps individuals to develop critical thinking skills, enabling them to navigate complex ethical issues and make informed decisions.
- Value education can be taught through various educational strategies, including classroom instruction, extracurricular activities, and community service projects.
- It can also be integrated into the curriculum of various academic disciplines, such as history, literature, and philosophy.
Also Read : Approaches of Counselling
In summary, values are beliefs or principles that guide our behavior and decision-making. Value education is the process of teaching and instilling positive values and character traits in individuals, with the objective of promoting positive behavior, attitudes, and ethics. Value education is important because it helps individuals to develop a strong sense of ethics and responsibility, promotes social cohesion, and helps individuals to develop critical thinking skills.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita