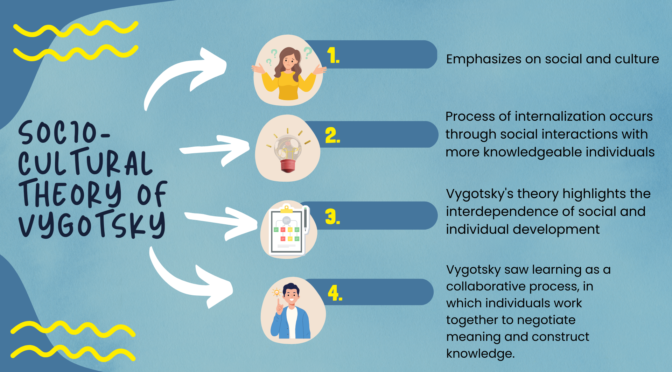
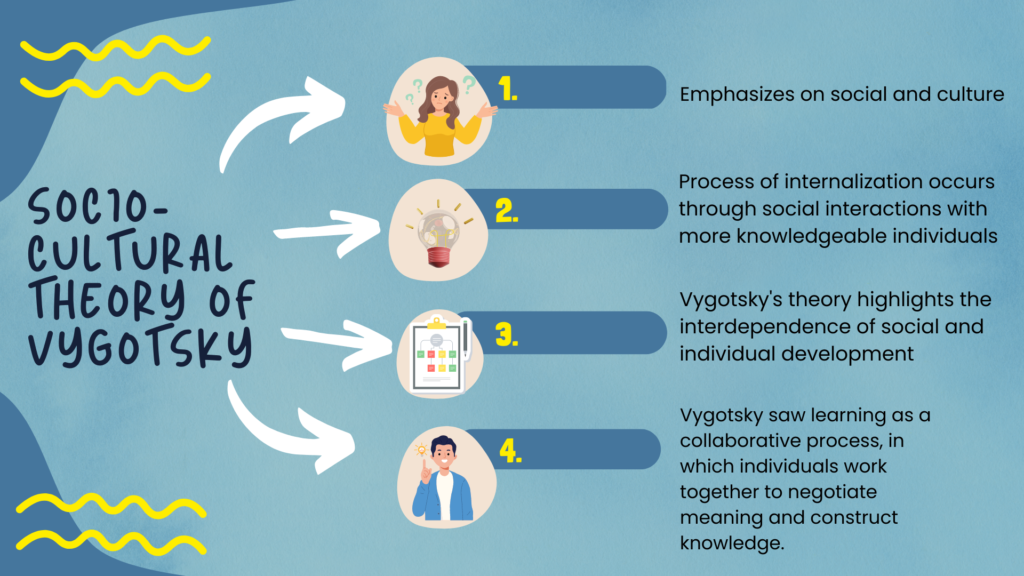
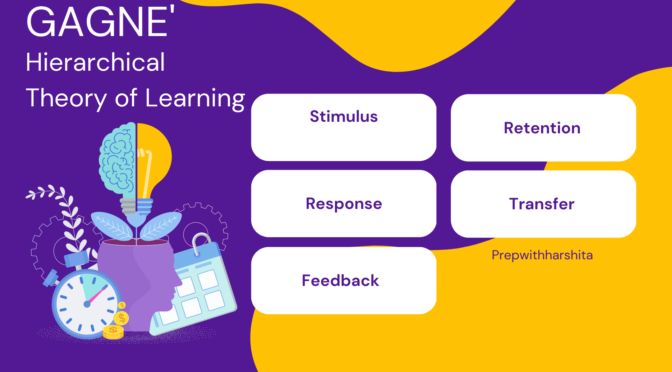
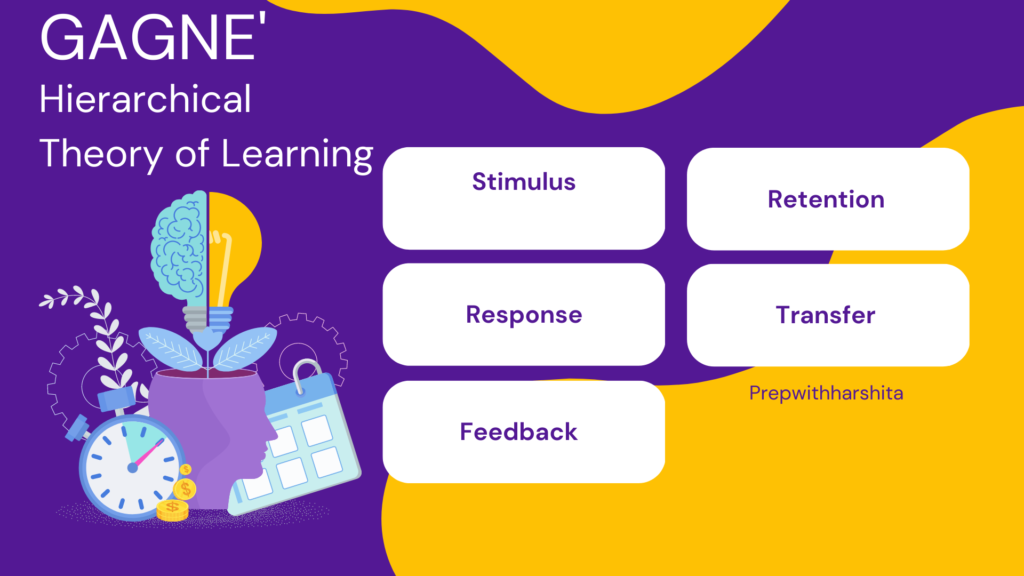
Intelligence is a complex construct that is influenced by a variety of factors. It is always said that Nature and nurture both affect intelligence.
Nature refers to heredity and nurture to
environment. At present, researchers agree that individual differences in intelligence are clearly the result of the interplay between genetic factors and the environmental conditions
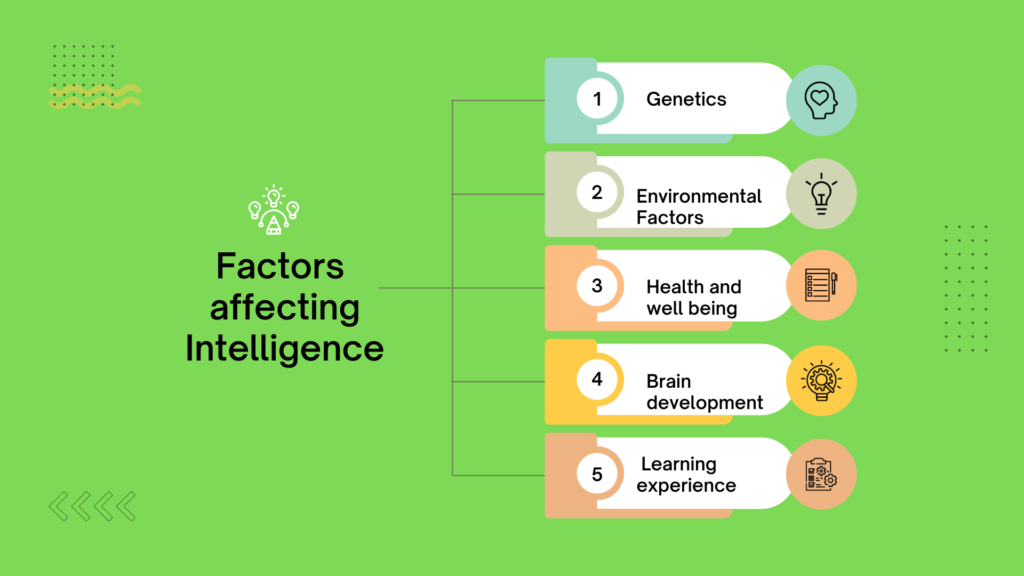
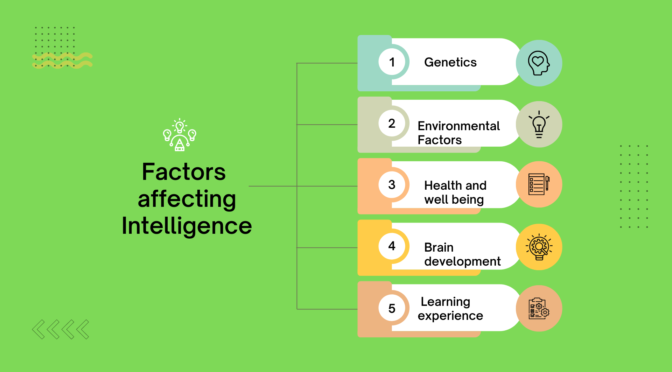
Here are some of the most important factors that can impact intelligence:
- Genetics: Intelligence is partially influenced by genetic factors. Certain genes may be associated with higher levels of cognitive ability and thus higher intelligence.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as nutrition, stress, and exposure to toxins can impact the development of the brain and therefore affect intelligence. There is evidence that environmental deprivation lowers intelligence while rich nutrition, quality schooling, and good family background increase intelligence.
- Brain development: The development of the brain, including the growth of brain structures and the formation of neural connections, can significantly impact intelligence.
- Health and well-being: Good health and overall well-being, including proper nutrition, exercise, and sufficient sleep, can contribute to higher levels of intelligence. A healthy diet will lead to better mental health and intelligence.
- Learning experiences: Formal education and informal exposure to new information and ideas, can have a significant impact on intelligence. With new learning and better ideas, the person becomes more intelligent.
- Emotional and social intelligence: Emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and regulate emotions is important. Social intelligence, the ability to understand and navigate social relationships, is also an important component of overall intelligence.
Also Read: Assessment Techniques of Personality
Intelligence is not determined solely by any one of these factors, but by the interplay and combination of all of these factors. Additionally, intelligence is a dynamic construct that can change and develop over time.