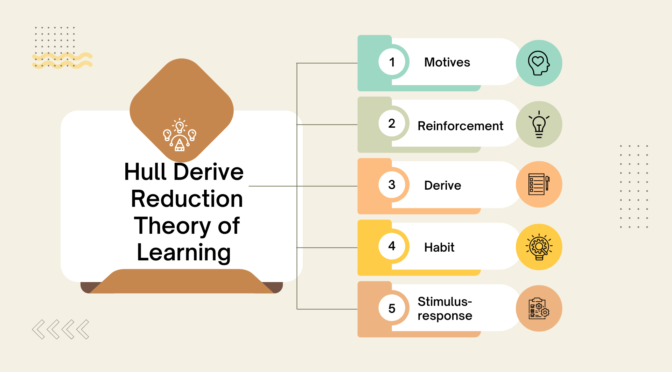
The Hull reduction theory of learning refers to the psychological theory proposed by Clark Hull in the 1930s and 1940s. It suggests that behavior is the result of a combination of drives, habits, and motives that are motivated by a need for reward or satisfaction. The theory proposes that learning occurs through a process of trial and error and reinforcement, and that behavior is shaped by the consequences of our actions.
According to Hull’s theory, the strength of a drive, habit, or motive is determined by its associated reinforcement value, which is in turn based on the subjective value of the reward or satisfaction obtained from the behavior. The theory also suggests that behavior is influenced by the individual’s history of reinforcement, with the frequency and timing of rewards affecting the strength of the drive, habit, or motive.
Hull’s reduction theory of learning is one of the early learning theory in psychology and remains an important influence in the field, particularly in the area of motivation and reinforcement.
Also Visit My YouTube Channel : Prep With Harshita
Features of Hull Reduction Theory of Learning :
- Drive reduction: Hull’s theory proposes that behavior is motivated by drives, which are based on physiological needs such as hunger, thirst, and the need for sleep. The theory suggests that the strength of a drive increases with deprivation and decreases with satisfaction.
- Reinforcement value: The reinforcement value of a behavior is the subjective value of the reward or satisfaction obtained from the behavior. Hull’s theory suggests that the strength of a drive, habit, or motive is determined by its associated reinforcement value.
- Habit strength: Hull’s theory proposes that habits are formed through repeated behavior and reinforcement, and that the strength of a habit increases with repetition and reinforcement.
- Stimulus-response relationships: Hull’s theory suggests that behavior is determined by the strength of the drive, habit, or motive, as well as the individual’s response tendencies and the properties of the stimulus.
- Trial-and-error learning: Hull’s theory suggests that learning occurs through a process of trial and error and reinforcement, with behavior being shaped by the consequences of our actions.
- Drive-reducing stimuli: Hull’s theory proposes that drive-reducing stimuli, such as food or water, have a higher reinforcement value than other stimuli and are more likely to elicit a drive-reducing response.
- Drive-increasing stimuli: Hull’s theory suggests that drive-increasing stimuli, such as hunger or thirst, increase the strength of a drive and increase the likelihood of a drive-reducing response.
These features of Hull’s reduction theory of learning highlight its focus on the role of reinforcement and drive in shaping behavior and its emphasis on the interaction between physiological needs and reinforcement in the learning process.
Also Read : Kothari Commission