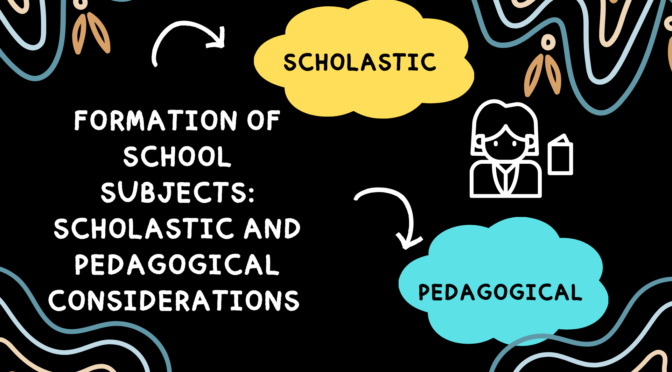
The formation of school subjects involves both scholastic (academic) and pedagogical (educational) factors. Scholastic considerations relate to the academic content and knowledge within a subject, while pedagogical considerations involve the methods and approaches used to teach and assess that content.
Here are some key aspects of the formation of school subjects:
Curriculum Development:
- Scholastic Consideration: Subject formation begins with defining the academic content that students are expected to learn. This involves identifying key concepts, theories, and skills within a particular field.
- Pedagogical Consideration: Curriculum developers must also consider how to effectively deliver the content. This includes selecting appropriate teaching methods, resources, and assessments that align with educational goals.
Educational Goals and Objectives:
- Scholastic Consideration: Making clear educational goals helps understand what students should know and be able to do in a given subject. These goals are based on academic standards and the desired outcomes of education.
- Pedagogical Consideration: Pedagogical considerations involve determining how to achieve these goals through instructional strategies, classroom activities, and assessments.
Interdisciplinary Connections:
- Scholastic Consideration: Subjects are often interconnected, and identifying these connections is important in providing a holistic education. For example, understanding the historical context of a scientific discovery may involve knowledge from both history and science.
- Pedagogical Consideration: Teachers can use interdisciplinary approaches to enhance students’ understanding by integrating content from different subjects. This approach encourages a more comprehensive and integrated understanding of topics.
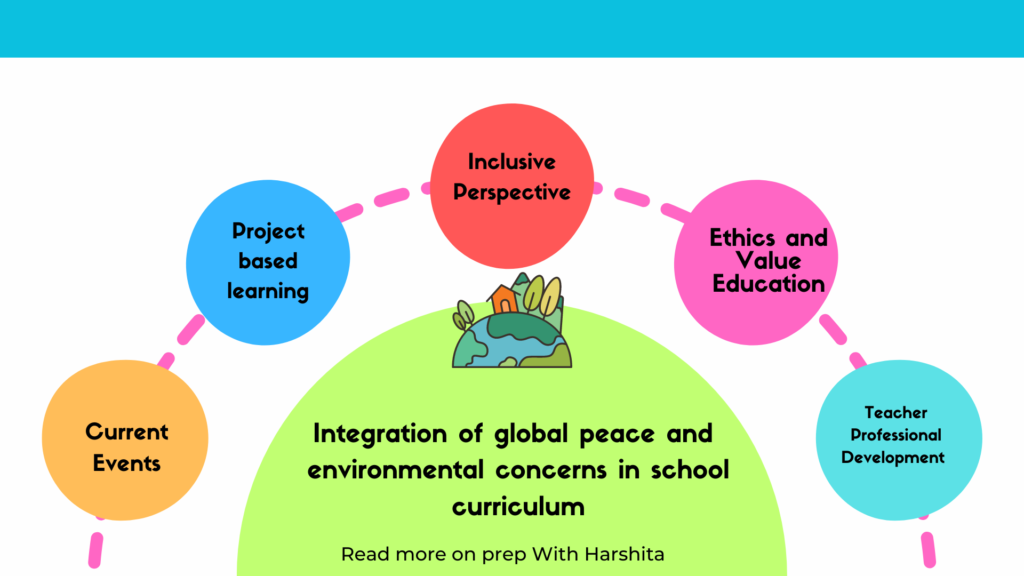
Teacher Training and Professional Development:
- Scholastic Consideration: Teachers need expertise in the content they are teaching. This includes staying updated with developments in the field and deepening their understanding of subject matter.
- Pedagogical Consideration: Teachers also need training in effective instructional strategies, classroom management, and assessment techniques. Professional development opportunities support ongoing improvement in pedagogical skills.
Assessment and Evaluation:
- Scholastic Consideration: Defining the criteria for assessing student learning is essential. This involves understanding how to measure students’ understanding, skills, and application of knowledge in a subject.
- Pedagogical Consideration: Teachers need to choose assessment methods that align with instructional goals and provide valuable feedback to students. This could include a mix of formative and summative assessments.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita

Also Read: Effective Learning of various disciplines