A competency-based model of curriculum design is an educational approach that emphasizes the mastery of specific competencies or skills as the primary focus of instruction.
In this model, the curriculum is designed around the knowledge, skills, and abilities that students need to acquire in order to be successful in a particular field or profession.
History and Origin of Competency Based Model of Curriculum
- The origins of the competency-based model of curriculum design can be traced back to the work of Benjamin Bloom. He was an educational psychologist who developed the taxonomy of educational objectives in the 1950s.
- Bloom argued that learning objectives should be specific and measurable, and that assessments should be aligned with those objectives.
- The competency-based approach to curriculum design gained popularity in the 1970s and 1980s. The educators began to focus more on the development of skills and abilities that were relevant to the workplace. The idea was to shift the focus from what students knew to what they could do with that knowledge.
Since then, the competency-based model of curriculum design has been refined and adapted by many educators and institutions. Today, it is used in a variety of settings, including K-12 education, higher education, and workforce training programs.
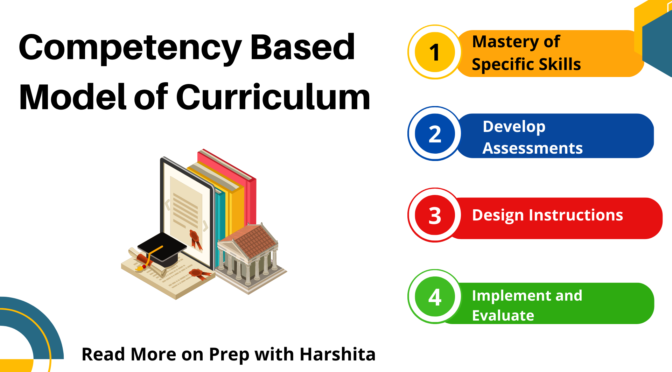
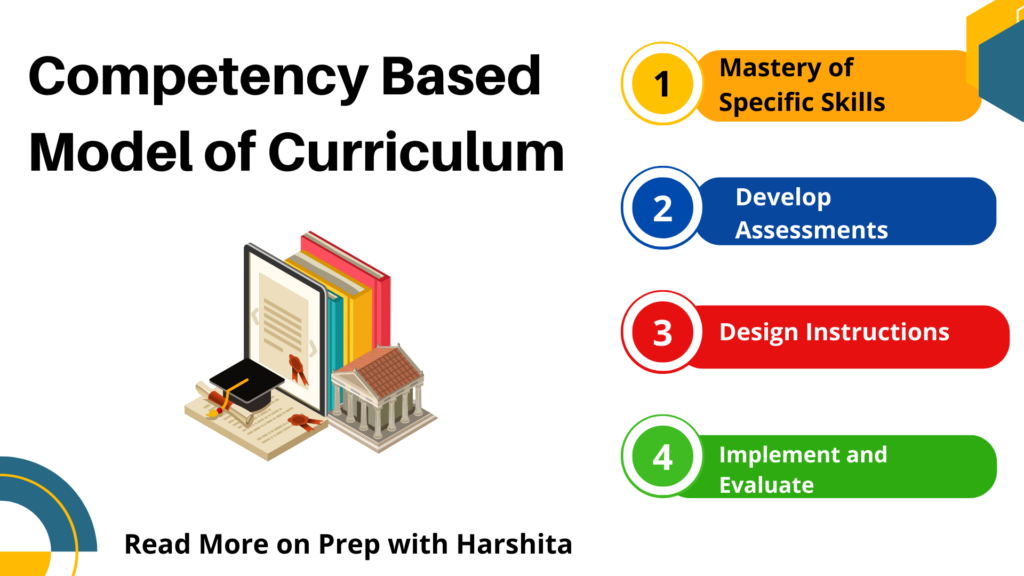
Here is a more detailed explanation of the components of this model:
- Identify the competencies: The first step in designing a competency-based curriculum is to identify the specific competencies that students need to master. This involves analyzing the skills and knowledge required for success in a particular field or profession, as well as considering any relevant standards or regulations.
- Define the learning objectives: Once the competencies have been identified, the next step is to define clear and measurable learning objectives for each competency. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, an objective for a competency in project management might be “Students will be able to create a project plan that includes a timeline, budget, and resource allocation.”
- Develop assessments: After defining the learning objectives, assessments must be developed that measure students’ mastery of each competency. These assessments should be aligned with the learning objectives and should measure both knowledge and skills. For example, a competency in public speaking might be assessed through a speech that students deliver in front of the class, while a competency in data analysis might be assessed through a written report or presentation that demonstrates students’ ability to analyze and interpret data.
- Design instruction: Once the learning objectives and assessments have been developed, instruction must be designed. It will help students develop the knowledge and skills necessary to master each competency. This may involve a variety of instructional strategies, such as lectures, discussions, group work, and hands-on activities. Instructional materials should be aligned with the learning objectives and assessments. It should be designed to help students develop the knowledge and skills necessary to perform well on the assessments.
- Implement and evaluate: The final step in the model is to implement the curriculum. Also to evaluate its effectiveness in helping students master the targeted competencies. This may involve collecting data on student performance on assessments, as well as gathering feedback from students, teachers, and other stakeholders. This information can be used to make adjustments to the curriculum . Changes can be made in instructional strategies as needed, in order to better support student learning.
Overall, It is designed to ensure that students acquire the specific knowledge and skills they need to succeed in their chosen field or profession. It also provide them with opportunities to apply that knowledge and those skills in real-world settings.
By focusing on the mastery of competencies rather than the acquisition of knowledge, this model can help prepare students for success in a rapidly changing job market.
Also Read : Hidden Curriculum
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita