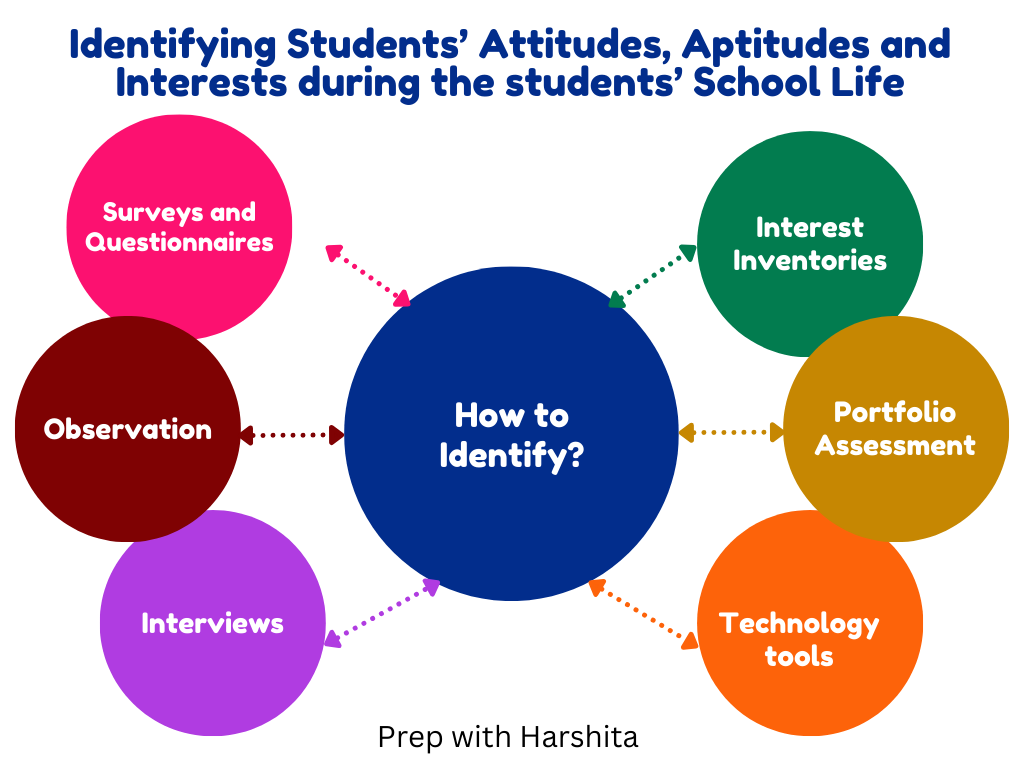
Identifying students’ attitudes, aptitudes, and interests during the students’ school life is important for their personal and academic development. Understanding these aspects helps educators alter their teaching methods, provide appropriate guidance, and create a better learning environment.
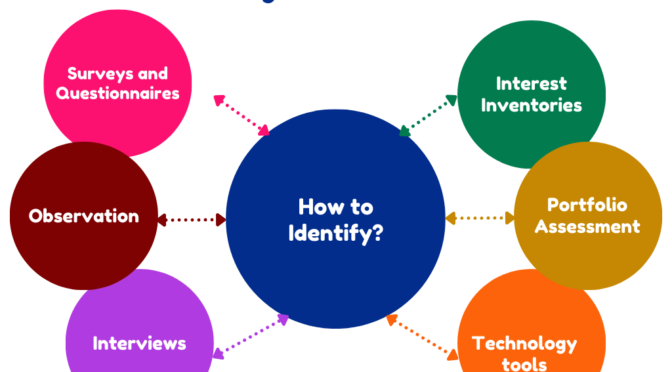
Strategies and methods to identify students’ attitudes, aptitudes, and interests during their school life:
Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Administer surveys or questionnaires to students to gather information about their interests, hobbies, and preferences.
- Include questions about their favorite subjects, extracurricular activities, and career aspirations.
Observation:
- Teachers can observe students in various settings, both inside and outside the classroom, to identify their attitudes and behaviors.
- Note how they engage with different subjects, tasks, and peers.
Interviews:
- Conduct one-on-one interviews with students to explore their thoughts, feelings, and aspirations.
- Encourage open and honest communication to gain insights into their attitudes toward learning and school life.
Portfolio Assessment:
- Have students create portfolios showcasing their best work, projects, and accomplishments.
- Analyze the content to identify patterns and preferences related to their aptitudes and interests.
Interest Inventories:
- Use interest inventories or aptitude tests to assess students’ preferences and strengths.
- These assessments can provide quantitative data to complement qualitative observations.
Classroom Activities and Projects:
- Design classroom activities and projects that allow students to explore different subjects and areas of interest.
- Pay attention to their enthusiasm and engagement levels during these activities.
Technology Tools:
- Use educational technology tools that incorporate analytics to track students’ online learning preferences and performance.
- Analyzing digital interactions can offer additional insights.
Career Counseling and Guidance:
- Provide access to career counseling services to help students explore potential career paths based on their interests and aptitudes.
- Guest speakers and field trips can also expose students to various professions.
Also Read : Distinction among attitude, Aptitude and interest
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita