English is a complex and rich language, with many linguistic characteristics that make it unique.
Here are some of the most notable linguistic characteristics of English:
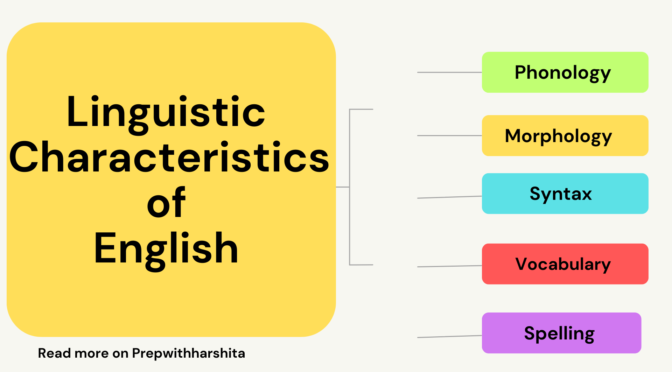
- Phonology:
English has a complex phonological system with over 40 distinct phonemes (individual speech sounds). It has five vowel sounds and twenty-four consonant sounds, and it has a stress-timed rhythm, which means that stressed syllables tend to occur at regular intervals. English also has some unique features in its pronunciation, such as the use of aspiration in voiceless plosives (e.g., “pin” vs. “spin”) and the glottal stop (e.g., “uh-oh”).
- Morphology:
English has a relatively simple morphology compared to many other languages. It has fewer inflections (word endings that indicate tense, case, or gender) than many other languages. Nouns are usually pluralized by adding “-s” or “-es,” and verbs are typically conjugated by adding “-s” or “-ed.” English also uses auxiliary verbs (e.g., “be,” “have,” “do”) to form tense and voice, and it has irregular verb forms (e.g., “go” → “went,” “be” → “was/were”).
- Syntax:
English has a relatively flexible syntax, meaning that it allows for a variety of word orders in sentences. English also uses auxiliary verbs and prepositions to indicate tense, mood, voice, and grammatical relationships between words. In addition, English often uses inversion (e.g., “Did you see the movie?” instead of “You did see the movie?”) and passive voice (e.g., “The book was read by the student” instead of “The student read the book”).
- Vocabulary:
English has a vast vocabulary, with over 170,000 words in current use and countless more obsolete or archaic words. English vocabulary has been heavily influenced by other languages, particularly Latin, Greek, and French, but also Arabic, German, and many others. English also has many loanwords, which are words borrowed from other languages, such as “sushi” from Japanese, “entrepreneur” from French, and “schadenfreude” from German.
- Spelling:
English spelling is notoriously irregular, with many words having multiple acceptable spellings and many exceptions to spelling rules. This is because English spelling has changed over time, and it reflects the influences of different languages and dialects. For example, the word “through” is pronounced differently than it looks like it should be, and the word “bough” and “cough” are pronounced differently but spelled similarly.
- Pragmatics:
English has a rich set of pragmatic conventions, including idiomatic expressions, indirect speech acts, and various forms of politeness and social signaling. These pragmatic conventions can vary depending on the social context and can be difficult for non-native speakers to master. For example, saying “Could you pass me the salt?” can be more polite than saying “Pass me the salt,” and saying “I’m afraid I can’t come” can be a polite way to decline an invitation.
- Dialects:
English is spoken in many different dialects, each with its own unique vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar. Some of the most notable dialects include British English, American English, Australian English, and Indian English. These dialects can be mutually intelligible (meaning that speakers of different dialects can understand each other), but they can also have significant differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
In summary, English is a complex and diverse language with many linguistic characteristics that make it unique. Its phonology, morphology, syntax, vocabulary, spelling, pragmatics, and dialects all contribute to its rich and varied character.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita
Also Read : Remedial Teaching