In educational administration, leadership can be broadly categorized into administrative leadership and instructional leadership. These two types of leadership play distinct but complementary roles in the effective functioning and improvement of educational institutions. Let’s explore each type:
Administrative Leadership:
Administrative leadership involves the management and coordination of the administrative functions of an educational institution. It focuses on organizational efficiency, resource management, policy implementation, and the day-to-day operations of the school.
Key Responsibilities:
- Organizational Management: Overseeing the structure and functioning of the educational institution, including administrative processes and support services.
- Resource Allocation: Managing financial resources, human resources, and physical facilities to ensure proper output.
- Policy Implementation: Ensuring that institutional policies and procedures are effectively communicated, implemented, and adhered to by all stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks, maintaining a safe and conducive environment for learning.
Characteristics of Administrative Leaders:
- Organizational Skills: Strong organizational and managerial skills to ensure the smooth running of the institution.
- Decision-Making: Effective decision-making abilities, especially in matters related to resource allocation and policy implementation.
- Communication: Clear communication skills to convey policies and expectations to staff, students, and other stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Efficient at problem-solving and handling day-to-day challenges that arise within the institution.
Instructional Leadership
Instructional leadership is focused on enhancing teaching and learning processes within the educational institution. It involves providing guidance, support, and supervision to educators to improve instructional practices and student outcomes.
Also Read : Styles of Educational Leadership
Key Responsibilities:
- Curriculum Development: Collaborating with educators to develop and improve curriculum content and instructional strategies.
- Teacher Professional Development: Providing opportunities for teacher training, mentoring, and ongoing professional development to enhance teaching skills.
- Student Assessment: Monitoring and improving student assessment methods to ensure accurate measurement of student progress.
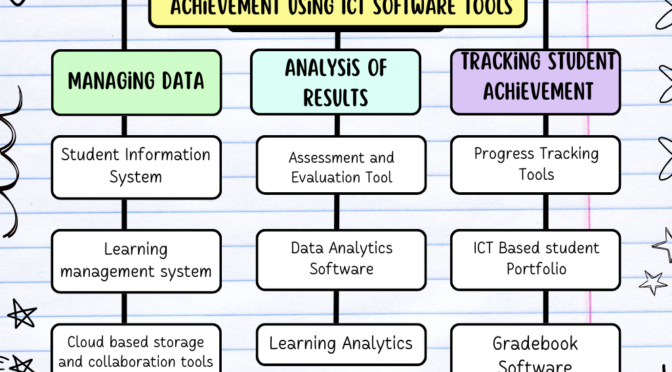
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data to inform instructional decisions, identifying areas of improvement, and implementing strategies to enhance student achievement.
Characteristics of Instructional Leaders:
- Pedagogical Knowledge: Strong understanding of teaching and learning principles, current educational trends, and effective instructional strategies.
- Collaboration: Collaborative and supportive, fostering a culture of continuous learning among educators.
- Visionary Leadership: A vision for educational excellence, inspiring and motivating educators to achieve high standards.
- Data Literacy: Proficient in analyzing educational data to make informed decisions about instructional practices.
Integration of Administrative and Instructional Leadership:
Effective educational leadership often requires a combination of both administrative and instructional leadership skills. Successful school leaders integrate these two types of leadership to create a balanced and supportive environment that promotes organizational effectiveness, resource management, and continuous improvement in teaching and learning.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita