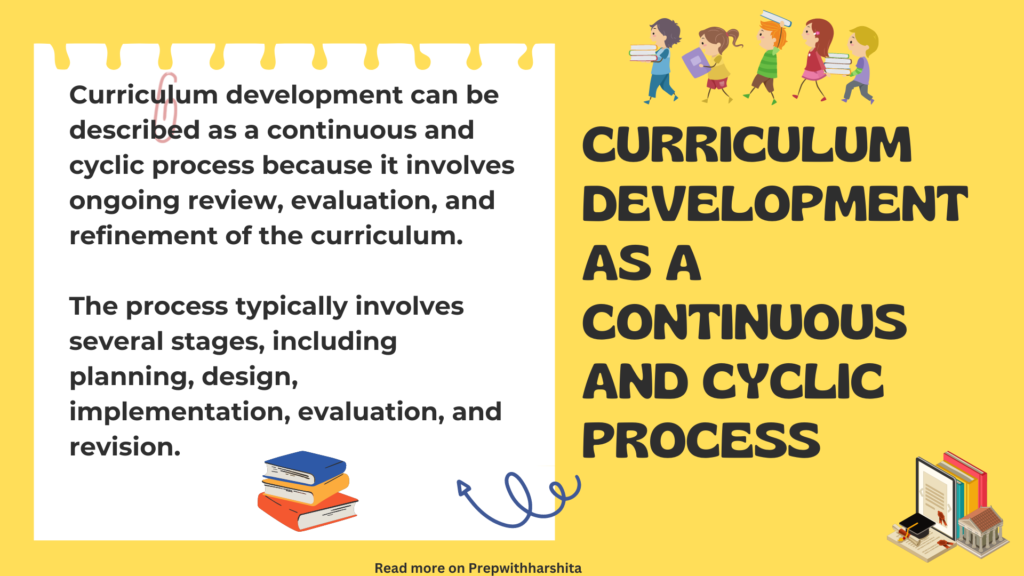
Curriculum development can be described as a continuous and cyclic process because it involves ongoing review, evaluation, and refinement of the curriculum.
Process of Curriculum Development
The process typically involves several stages, including planning, design, implementation, evaluation, and revision. Each of these stages informs the next, and the process is ongoing, with feedback loops and continuous improvement.
Here are some ways in which curriculum development can be described as a continuous and cyclic process:
- Planning: In the planning stage, the curriculum development team sets the goals and objectives for the curriculum. They also identify the content and resources that will be used to teach the curriculum. Planning is an ongoing process that involves continuous review and refinement.
- Design: In the design stage, the curriculum development team creates the structure and format of the curriculum. This stage includes developing lesson plans, learning activities, and assessments. Design is an ongoing process because the curriculum is revised as new information and resources become available.
- Implementation: In the implementation stage, the curriculum is put into action. This stage involves teaching the curriculum to students and making adjustments as needed. Implementation is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and refinement.
- Evaluation: In the evaluation stage, the curriculum development team assesses the effectiveness of the curriculum. This stage also includes gathering feedback from students, teachers, and other stakeholders. Evaluation is an ongoing process that informs the revision stage.
- Revision: In the revision stage, the curriculum development team makes changes to the curriculum based on feedback and evaluation. This stage includes updating the goals and objectives, refining the content and resources, and adjusting the structure and format of the curriculum. Revision is an ongoing process that leads back to the planning stage.
Overall, curriculum development is a continuous and cyclic process that requires ongoing review, evaluation, and refinement. The process is not linear, and each stage informs the next, leading to continuous improvement and growth.
Also Visit: Prepwithharshita