Curriculum as Program (CAP) is an educational framework that emphasizes the design and organization of a curriculum as a structured and cohesive program. It is an approach that views curriculum development as a systematic process of planning, implementing, and evaluating educational programs.
In the CAP model, a curriculum is seen as a comprehensive program rather than a collection of isolated courses or subjects. It takes into consideration the learning objectives, content, instructional strategies, and assessment methods to create a coherent and integrated educational experience for students.
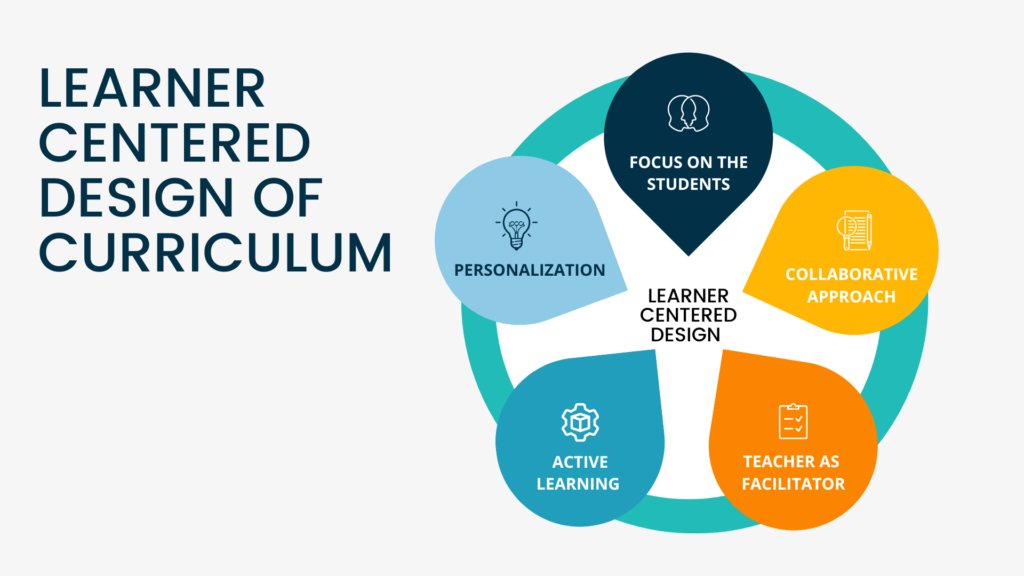
Here are some key components and principles associated with the Curriculum as Program approach:
- Goals and Objectives: CAP begins with clearly defined educational goals and objectives. These goals reflect the desired learning outcomes and provide a framework for curriculum development.
- Alignment: CAP emphasizes aligning the curriculum with the stated goals and objectives, as well as with the needs and expectations of the learners. The curriculum content and instructional strategies are carefully selected to ensure coherence and relevance.
- Sequencing and Progression: CAP considers the logical sequencing and progression of learning experiences. It focuses on structuring the curriculum in a way that enables students to build upon their knowledge and skills incrementally.
- Integration: CAP promotes the integration of various subject areas and disciplines to create meaningful connections and promote interdisciplinary learning. It seeks to break down the traditional compartmentalization of knowledge and encourages students to see the interrelatedness of different topics.
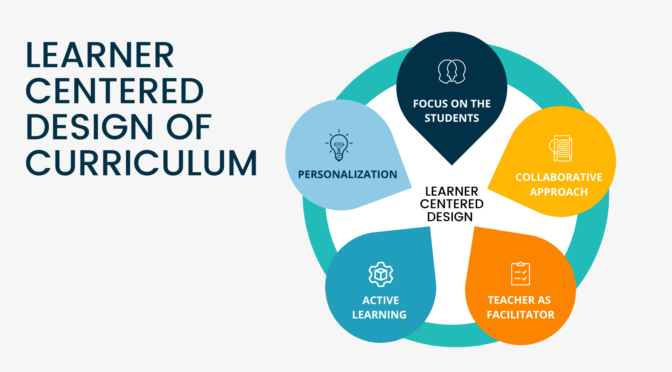
- Active Learning: CAP encourages active student engagement and participation in the learning process. It emphasizes learner-centered instructional approaches, such as problem-solving, project-based learning, and collaborative activities.
- Assessment and Evaluation: CAP incorporates ongoing assessment and evaluation strategies to measure student progress and provide feedback for improvement. It focuses on both formative and summative assessments aligned with the curriculum goals.
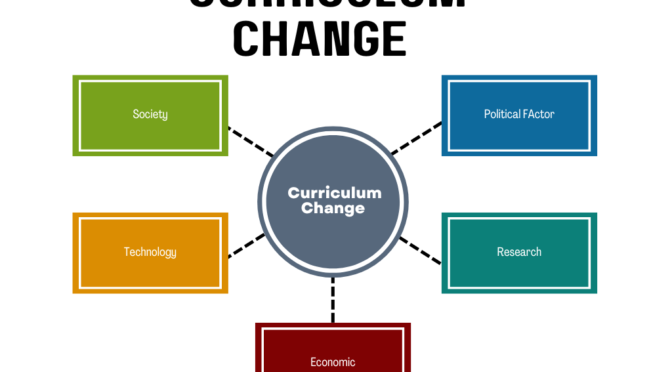
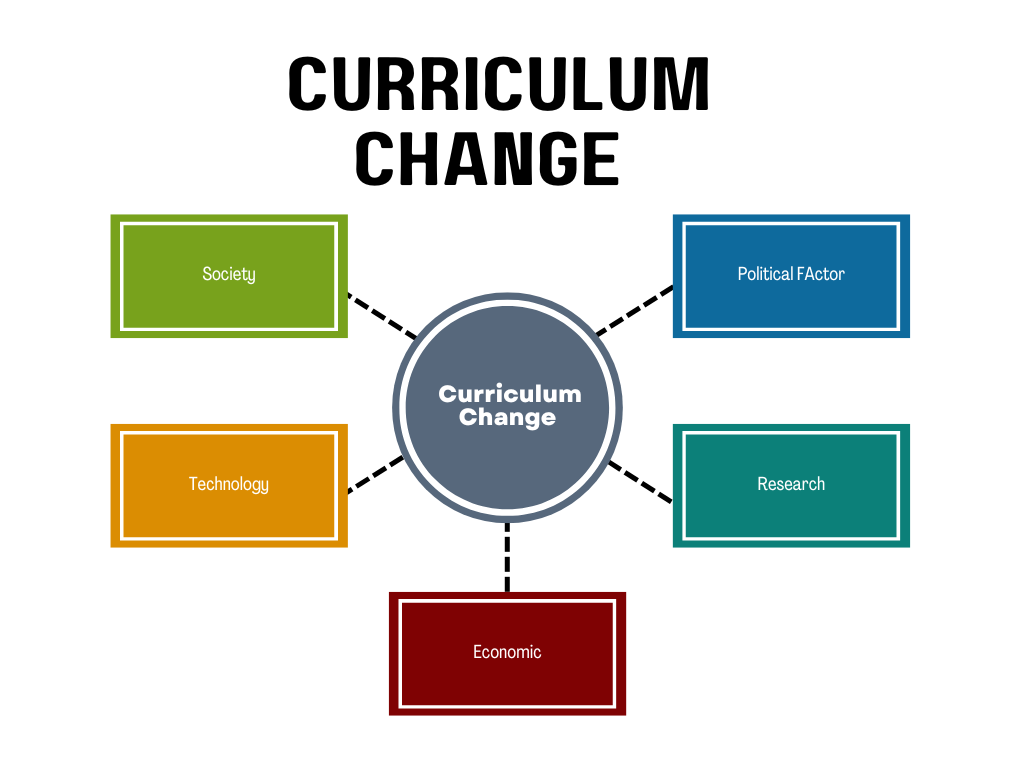
- Continuous Improvement: CAP recognizes the need for continuous evaluation and improvement of the curriculum. It involves gathering feedback from various stakeholders, including students, teachers, and administrators, to make necessary adjustments and enhancements.
By adopting the Curriculum as Program approach, educational institutions aim to create a well-designed, coherent, and purposeful curriculum that supports student learning and achievement. It encourages educators to view the curriculum as a dynamic and evolving program that adapts to the changing needs and demands of the learners and the society.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita
Also Read : Curriculum as Product