Optimal analysis refers to the process of analyzing and evaluating a situation or problem to identify the best possible solution or course of action. It involves taking into consideration all relevant factors and data, and using a systematic and logical approach to make informed decisions.
Optimal analysis typically involves using evidence-based practices, tools, and techniques to collect, analyze, and interpret data. The goal is to identify the most effective and efficient way to achieve a particular objective or outcome, while considering any constraints or limitations that may be present.
In the context of education planning, optimal analysis involves using data and evidence-based practices to inform decision-making and improve the effectiveness and efficiency of education programs.
Optimal analysis in education planning involves using data and evidence-based practices to inform decision-making and improve the effectiveness and efficiency of education programs.
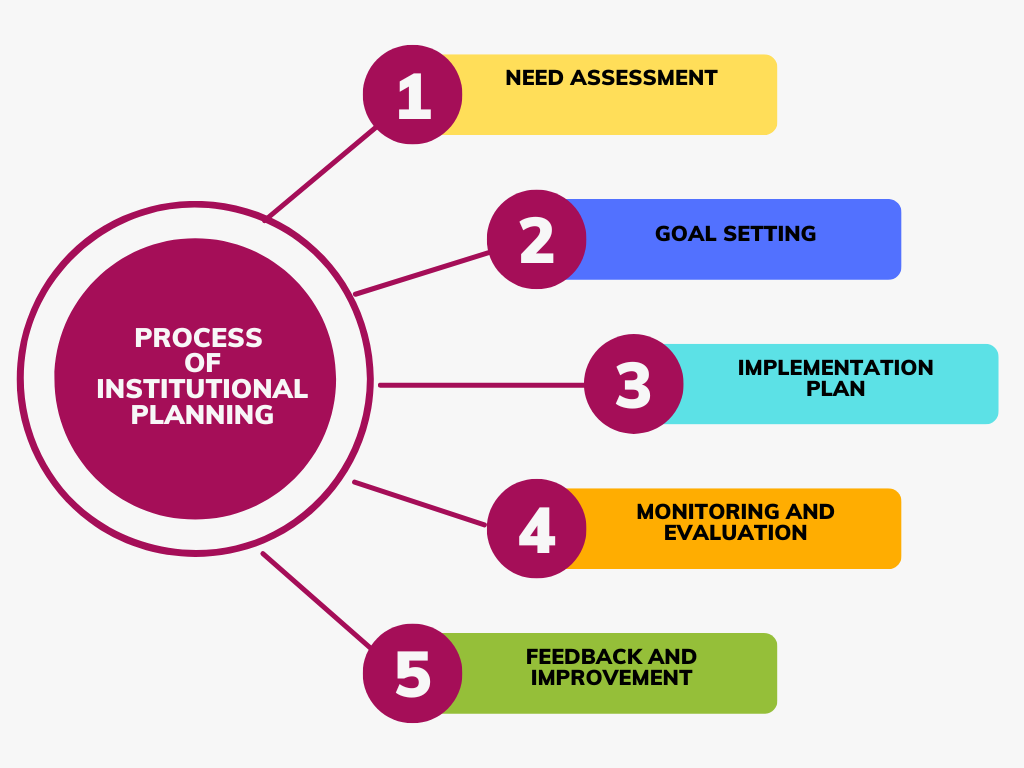
There are several key steps involved in optimal analysis in education planning, including:
- Data collection and analysis: Education planners must collect and analyze data to identify areas of need and to assess the effectiveness of existing programs. This may involve analyzing student performance data, conducting surveys or focus groups with students and educators, and reviewing research literature.
- Goal setting: Education planners must set clear and measurable goals for education programs based on the data and analysis conducted. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Program design: Education planners must design education programs that are aligned with the goals set and that are based on evidence-based practices. This may involve selecting or designing instructional materials, developing assessments, and selecting appropriate teaching strategies and methods.
- Implementation: Education planners must implement education programs effectively, providing adequate resources and support to educators and students. This may involve professional development for educators, providing appropriate technology and instructional resources, and ensuring that students have access to the resources they need to succeed.
- Evaluation: Education planners must evaluate the effectiveness of education programs and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that goals are being met. This may involve analyzing student performance data, conducting surveys or focus groups with students and educators, and reviewing research literature.
Also Read : Yashpal Committee

Also Visit : Prep with Harshita