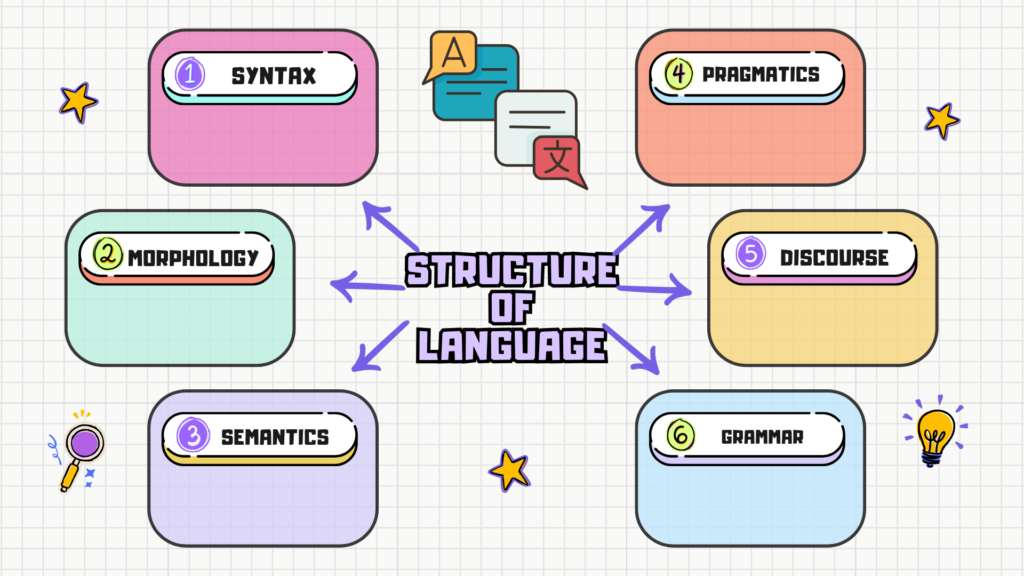
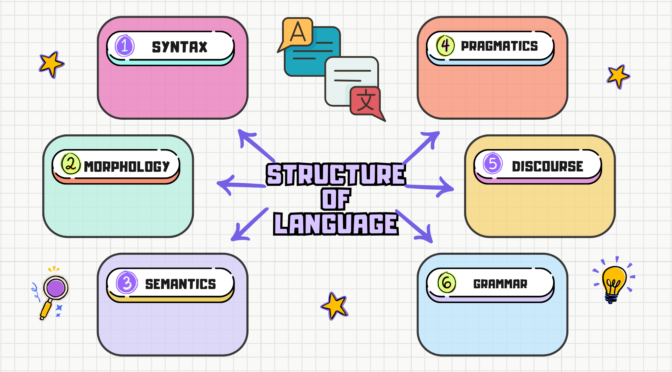
The structure of language refers to the organization and arrangement of linguistic elements, such as sounds, words, and sentences, to convey meaning. Linguists analyze language structure at various levels, ranging from the smallest units of sound to the overall organization of discourse. Here are some key components of the structure of language:
Phonetics and Phonology:
- Phonetics: Examines the physical properties of speech sounds, including their production, transmission, and reception.
- Phonology: Focuses on the study of the sound patterns and rules within a particular language, including how sounds interact and form phonemes.
Morphology:
Studies the structure and formation of words. Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning, and morphology explores how they combine to create words.
Syntax:
Deals with the structure of sentences and the rules governing how words are combined to form grammatically correct phrases and sentences.
Also Read : Difference between language and communication
Semantics:
Concerned with the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It explores how words and combinations of words convey meaning and how meaning is interpreted.
Pragmatics:
Examines the use of language in context and how context influences the interpretation of meaning. Pragmatics considers factors such as social roles, relationships, and the speaker’s intentions.
Grammar:
Encompasses both syntax and morphology and provides the rules for constructing grammatically correct sentences and words in a language.
Discourse:
Studies the organization and structure of extended stretches of language, such as conversations, narratives, and written texts. Discourse analysis examines how sentences and utterances connect to form coherent communication.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita