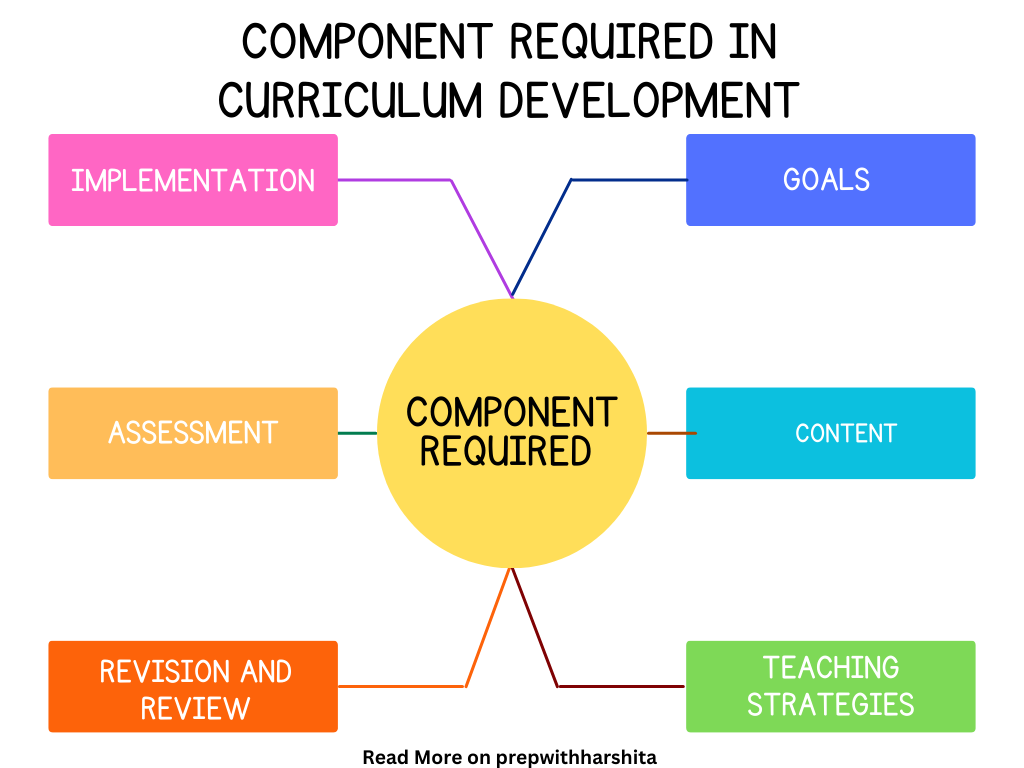
Curriculum development is a process that involves designing and developing an educational program that meets the learning needs of students. The following are the various components required in curriculum development:
- Goals and Objectives: These are the broad statements that describe the intended outcomes of the educational program. Goals and objectives provide a clear direction for the development of the curriculum and help to ensure that the program meets the needs of students.
- Content: This component includes the subject matter or the topics that the students will learn. The curriculum should cover the necessary concepts, skills, and knowledge required to achieve the program’s goals and objectives.
- Teaching and Learning Strategies: This component outlines the methods and techniques used to deliver the curriculum content to students. It includes instructional strategies, such as lectures, discussions, group work, projects, and multimedia resources.
- Assessment and Evaluation: This component involves the development of criteria and standards used to assess student learning and evaluate the effectiveness of the curriculum. It includes formative and summative assessments and methods for collecting feedback from students and teachers.
- Learning Resources and Materials: The curriculum should include a variety of learning resources. They can textbooks, workbooks, online resources, and other materials that support student learning.
- Teacher Professional Development: This component involves training teachers and educators on how to implement the curriculum effectively. It includes ongoing professional development opportunities to enhance their teaching skills and knowledge.
- Implementation Plan: This component outlines how the curriculum will be implemented in the classroom, including timelines, roles and responsibilities, and necessary resources.
- Revision and Review: The curriculum is regularly reviewed and updated to ensure it remains relevant and effective. The review process should involve feedback from students, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Involvement: The involvement of various stakeholders, such as teachers, parents, students, and community members, is essential in curriculum development to ensure that it meets the needs of all parties involved.
By including these components, curriculum developers can create a comprehensive and effective educational program that meets the needs of students, educators, and society as a whole.
Also Read: Critical Approach to Curriculum