Educational policy refers to a set of principles, guidelines, rules, and regulations that are developed and implemented to guide the functioning of the education system.
Educational policy is concerned with various aspects of education, such as access to education, curriculum development, teacher training, funding, assessment, and evaluation.
Policies are developed at different levels, including national, state, and institutional levels and they are aimed at achieving specific educational goals and objectives.
The development of educational policies involves the participation of various stakeholders, including policymakers, educators, parents, students, and community members.
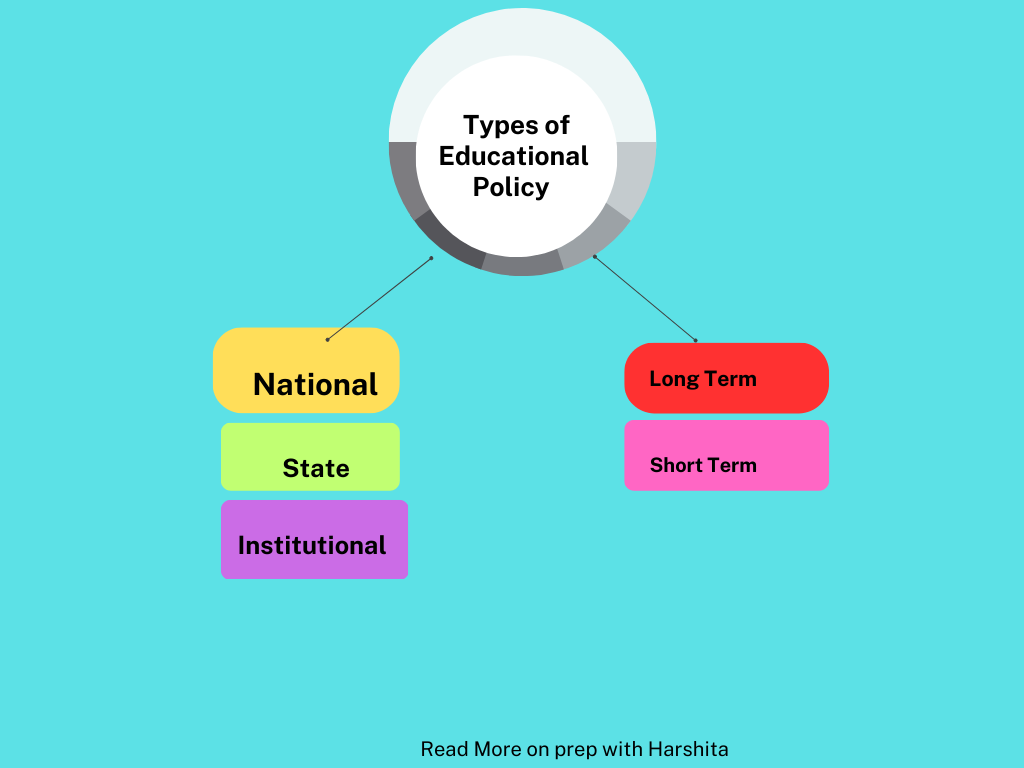
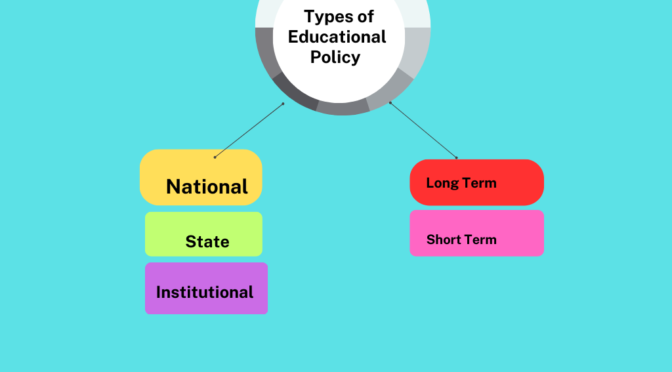
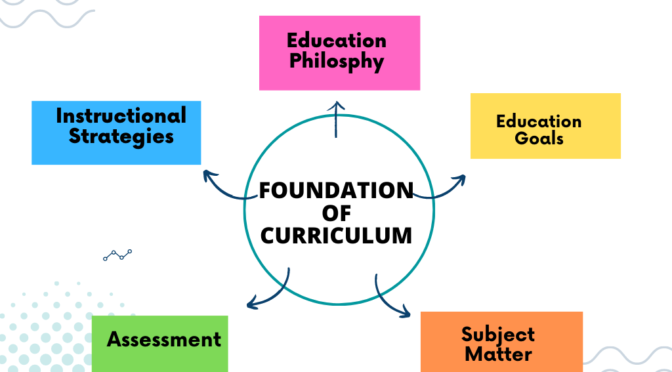
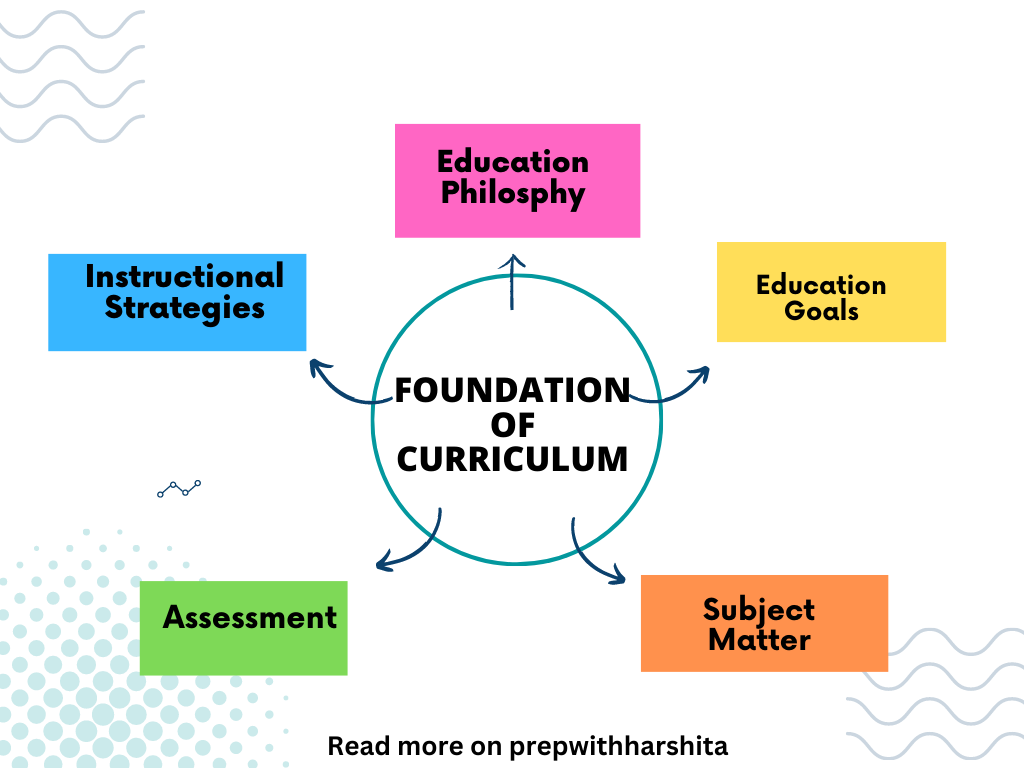
Types of Educational Policy:
National Level Policy
- National-level policies: The Ministry of Education is responsible for formulating and implementing educational policies at the national level. Some of the key national-level policies in India include:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: This policy aims to transform the education system in India and make it more inclusive, holistic, and multidisciplinary.
- Right to Education Act (RTE) 2009: This policy mandates free and compulsory education for all children between the ages of 6 and 14.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): This policy aims to provide universal elementary education to all children in the age group of 6-14 years.
State Level Policy
- State-level policies: Each state in India has its own education department responsible for formulating and implementing education policies. Some of the key state-level policies include:
- State Education Policy: This policy outlines the state’s vision for education and the strategies to achieve it.
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme: This policy provides free meals to children in government and government-aided schools.
- State Scholarship Scheme: This policy provides financial assistance to students from economically weaker sections to pursue their education.
Institutional Policy
- Institutional level policies: Educational institutions such as universities, colleges, and schools also have their own policies that govern their functioning. Some of the key institutional-level policies include:
- Admission Policy: This policy outlines the criteria and procedures for admission to the institution.
- Examination Policy: This policy outlines the rules and regulations for conducting examinations and evaluating students.
- Disciplinary Policy: This policy outlines the code of conduct and disciplinary procedures for students and staff.
Short Term Policy
- Short-term educational policies in India are designed to address immediate needs and challenges in the education system.
- These policies usually have a timeframe of a few years and focus on specific issues, such as increasing access to education, improving the quality of education, or enhancing learning outcomes.
- Short-term policies are typically aimed at achieving short-term goals and objectives.
- Short-term policies are usually focused on specific issues, such as providing free textbooks or improving classroom infrastructure.
Some examples of short-term educational policies in India are:
- Mid-day Meal Scheme: This policy provides free meals to children in government and government-aided schools to ensure that they receive adequate nutrition.
- National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme: This policy provides financial assistance to economically disadvantaged students to encourage them to complete secondary education.
- Digital India: This policy aims to promote the use of technology in education to enhance learning outcomes and access to education.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita
Long Term Policy
- Long-term educational policies in India are focused on achieving broader goals and objectives over a sustained period of time.
- These policies usually have a timeframe of several years or even decades, and they are aimed at transforming the education system in India to meet the changing needs of society.
- Long-term policies are typically aimed at achieving long-term goals and objectives.
- Long-term policies are more comprehensive and are aimed at addressing multiple issues in the education system, such as curriculum development, teacher training, and assessment and evaluation.
Some examples of long-term educational policies in India are:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: This policy aims to transform the education system in India and make it more inclusive, holistic, and multidisciplinary. The NEP 2020 has a long-term vision of making India a global knowledge superpower.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA): This policy aims to improve the quality of secondary education in India and increase the enrolment rate of students in the age group of 14-18 years.
- Skill India: This policy aims to provide vocational education and training to young people in India to enhance their employability and entrepreneurship skills.