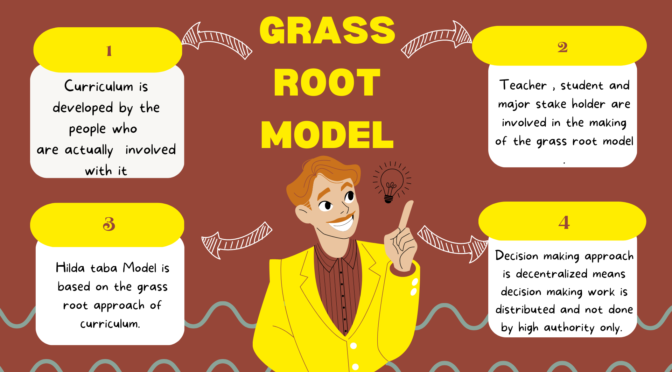
The grass-roots model of curriculum refers to an approach in which the design, development, and implementation of the educational curriculum are driven by the needs, experiences, and perspectives of teachers, students, and other stakeholders who are directly involved with the use of curriculum. This is a bottom up approach. This model is characterized by a decentralized approach, in which decision-making authority is distributed among different stakeholders. The goal of the grass-roots model is to create a curriculum that is relevant, meaningful, and according to the needs of the community, rather than being imposed from above.
Hilda Taba’s model is based on grass root approach. The model emphasizes a collaborative and democratic approach to curriculum development that involves all stakeholders, including teachers, students, administrators, and community members.
Key features of this model include:
- Community involvement: This model involves the active participation of community members in determining the educational needs and goals of the local area.
- Decentralization: The grass root model emphasizes decentralized decision making, with more power being given to local schools and communities to determine their own curricular needs and the power is not in a single hand.
- Relevance to need : The curriculum is developed with a focus on addressing the specific needs and challenges of the local community, making it more relevant and useful for students.
- Cultural sensitivity: The grass root model takes into account the cultural and linguistic background of the local community, ensuring that the curriculum is inclusive and culturally sensitive.
- Flexibility: This model allows for flexibility in the implementation of the curriculum, taking into account the unique needs and resources of each community.
Also Read : Tyler Model
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita