The economics of brain drain can be analyzed from different perspectives. Brain drain refers to the emigration of highly skilled or educated individuals from their home country to another country, often for better job opportunities or higher wages.
The perspective of Home Country
From the perspective of the home country, brain drain can have negative economic consequences.
Highly skilled and educated workers are often crucial to a country’s economic development, innovation, and productivity. When these individuals leave their home country, it can result in a loss of human capital, which can ultimately hinder economic growth.
Additionally, the cost of educating these individuals is borne by the home country, which means that brain drain can also result in a loss of public investment.
The perspective of the host country
On the other hand, from the perspective of the host country, brain drain can be beneficial.
Highly skilled and educated workers are often in demand, particularly in sectors such as technology, healthcare, and academia. These workers can contribute to the host country’s economy by creating jobs, generating tax revenue, and driving innovation.
For the Individuals themselves
For the individuals themselves, brain drain can be both positive and negative.
Positive: Emigrating to another country can result in higher wages, better job opportunities, and a higher standard of living.
Negative: Brain drain can also result in social and cultural isolation, as well as a loss of connection to one’s home country and community.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita
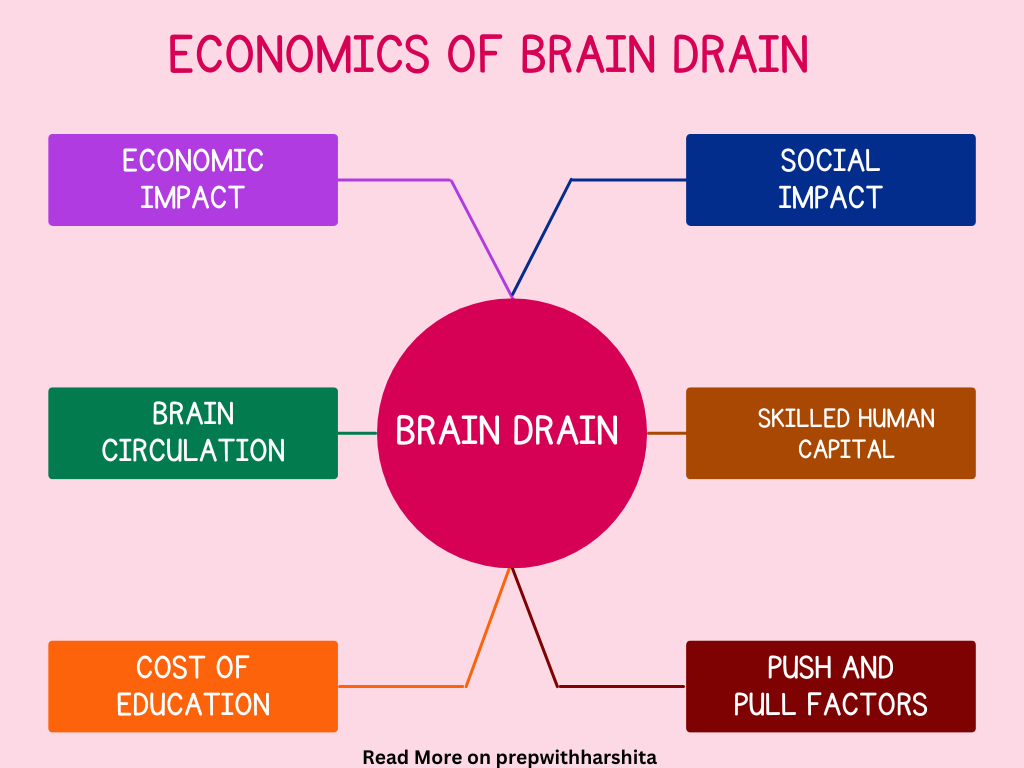
Features of Brain Drain :
The economics of brain drain is a complex phenomenon that involves a number of features, including:
- Skilled human capital: Brain drain typically involves the emigration of highly skilled and educated individuals, such as doctors, engineers, scientists, and other professionals.
- Push and pull factors: Brain drain is often driven by both push and pull factors. Push factors include poor economic conditions, political instability, limited job opportunities, and poor working conditions in the home country, while pull factors include better wages, job opportunities, and working conditions in the host country.
- Cost of education: In many cases, the cost of educating individuals who subsequently emigrate is borne by the home country. This means that brain drain can result in a loss of public investment and a drain on the home country’s resources.
- Brain circulation: Brain drain is not always a one-way process. Many highly skilled and educated individuals eventually return to their home country after working or studying abroad. This can result in a brain circulation process where individuals bring back new skills, knowledge, and experiences to their home country.
- Economic impact: Brain drain can have both positive and negative economic impacts on the home and host countries. The home country may experience a loss of skilled labor and a hindrance to economic growth, while the host country may benefit from an influx of skilled labor and the development of new industries and sectors.
- Social impact: Brain drain can also have significant social impacts on the individuals who emigrate, as well as their families and communities. This can include social and cultural isolation, a loss of connection to one’s home country, and a strain on family relationships.