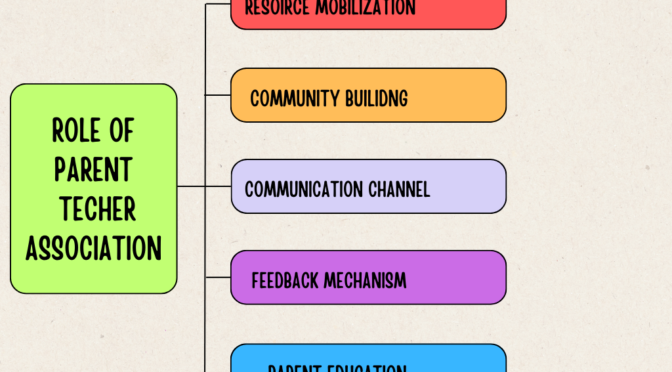
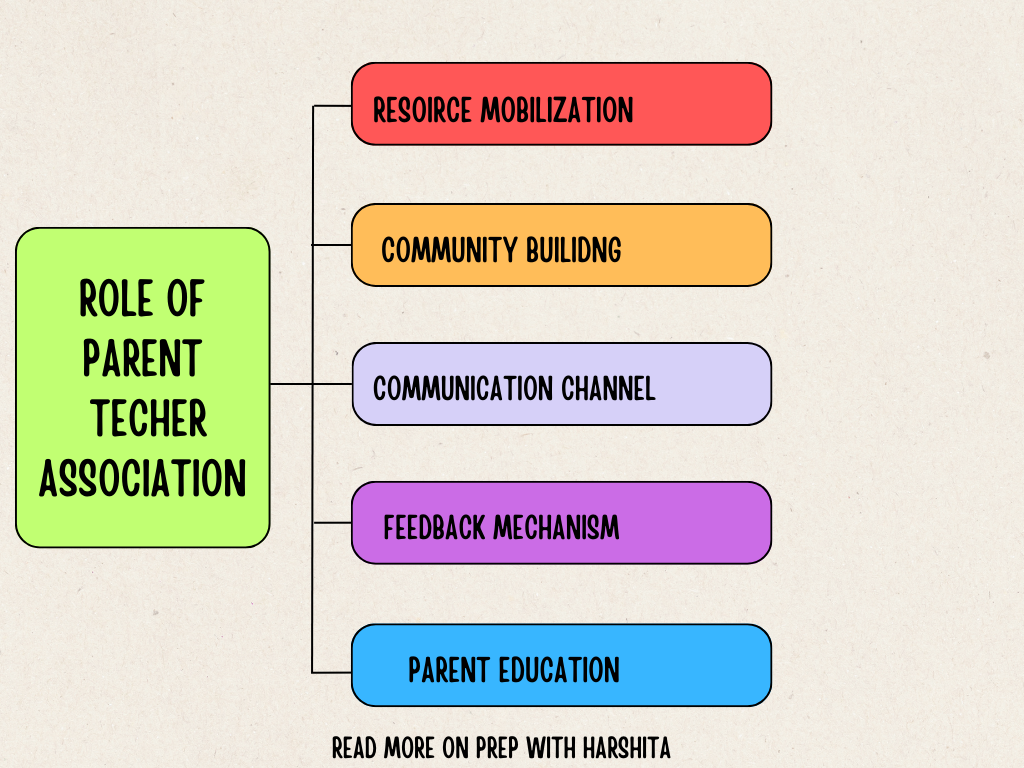
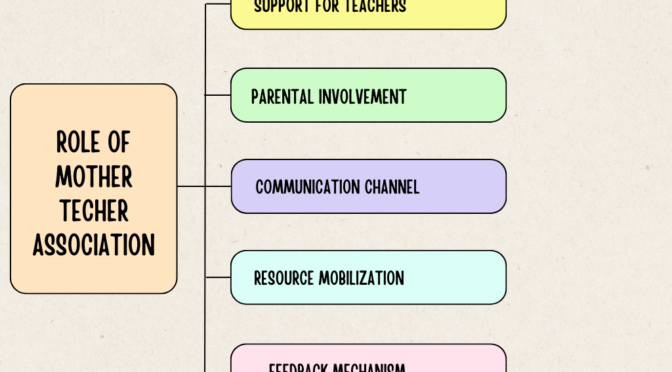
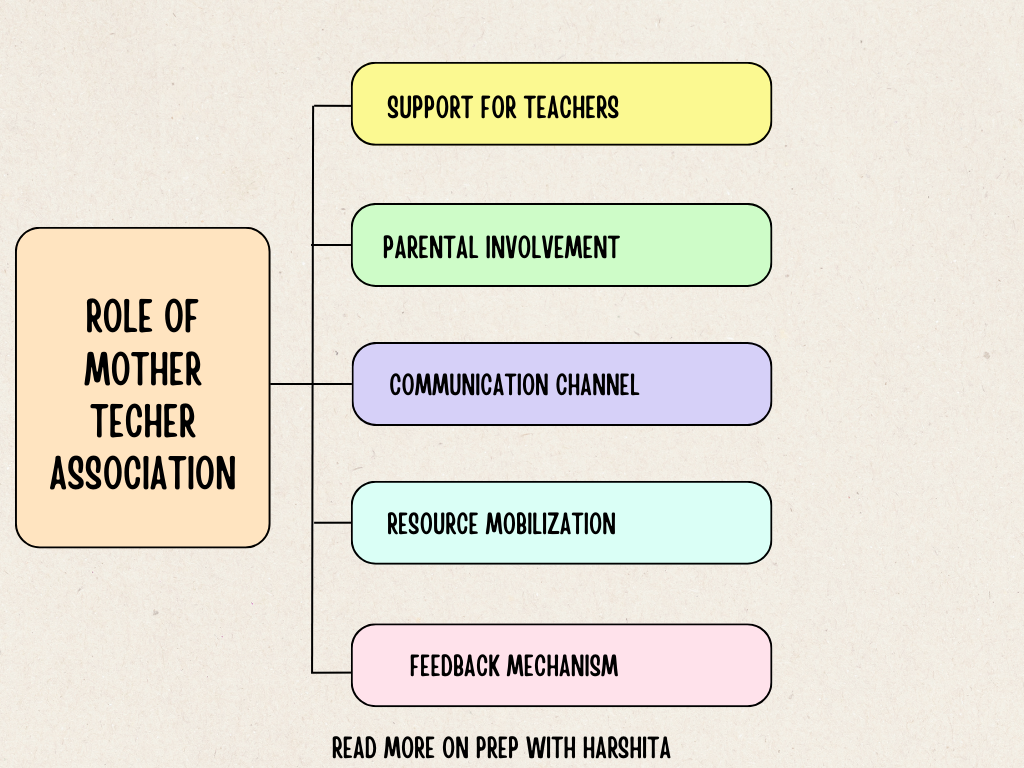
School environment refers to the physical, social, and psychological context in which learning and educational activities take place. It includes both tangible elements like buildings, classrooms, and facilities, as well as intangible aspects like the culture, relationships, and ethics of the school.
The school environment significantly influences the overall educational experience and plays a crucial role in shaping the academic, social, and emotional development of students. There are various types of school environments, each contributing to a unique learning atmosphere. Let’s learn more about school environment: Meaning and types
Types of School Environments:
Physical Environment:
- Classroom Design: The layout, organization, and aesthetics of classrooms impact the learning experience. Factors such as seating arrangements, lighting, and resources contribute to the physical environment.
- School Facilities: The quality of facilities, including libraries, laboratories, playgrounds, and sports facilities, influences the overall learning environment.
- Safety Measures: Physical safety and security measures contribute to a conducive learning atmosphere.
Also Read : School Discipline
Social Environment:
- School Culture: The shared values, beliefs, and traditions of a school community contribute to its culture. A positive school culture fosters a sense of belonging and encourages positive interactions.
- Peer Relationships: The dynamics among students, including friendships, collaborations, and conflicts, contribute to the social environment.
- Teacher-Student Relationships: The quality of interactions between teachers and students influences the classroom atmosphere and student engagement.
Read more on the next page…