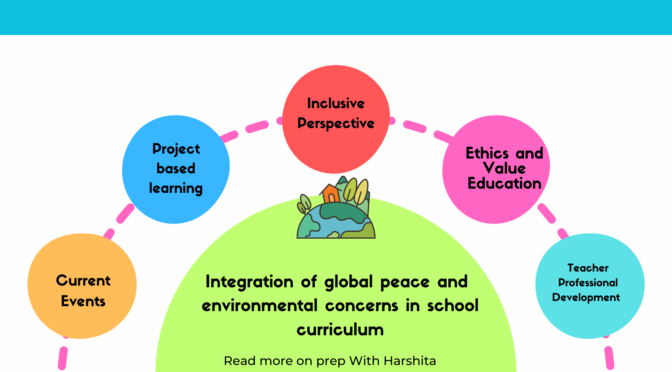
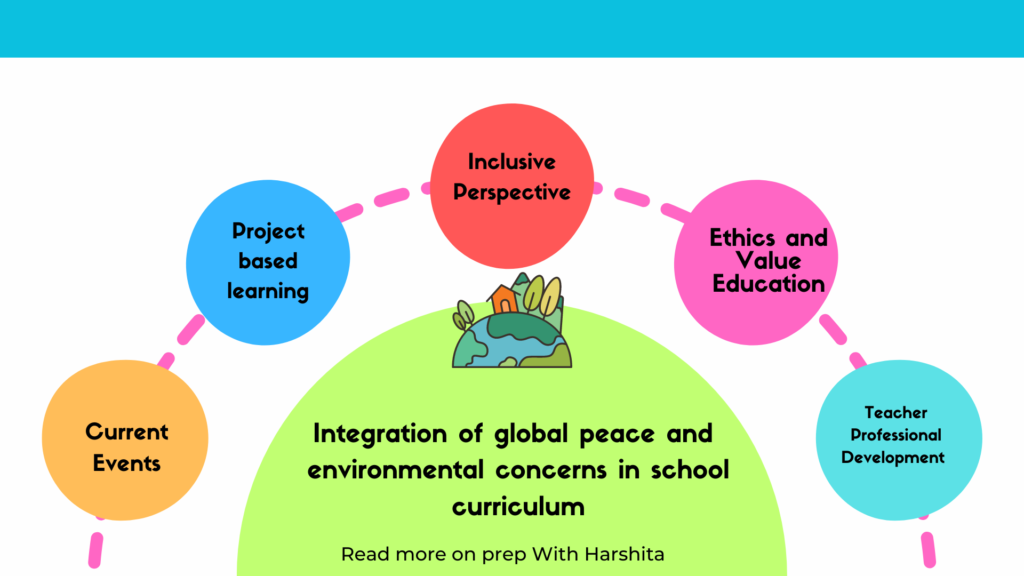
Integration of global peace and environmental concerns into school curriculum is important for fostering a generation of responsible and environmentally conscious citizens. Here are some suggestions on how to achieve this integration:
Interdisciplinary Approach:
Design interdisciplinary courses that combine elements of environmental science, geography, history, and social studies to provide a broader understanding of global peace and environmental issues.
Incorporate Current Events:
Include discussions on current global peace and environmental issues in various subjects. This can be achieved through regular updates, news articles, and case studies.
Project-Based Learning:
Implement project-based learning initiatives that require students to engage in real-world problem-solving related to global peace and environmental concerns. This could involve community projects, research assignments, or collaborative initiatives with local environmental organizations.
Inclusive Perspectives:
Ensure that curricula represent different perspectives on global peace and environmental issues. Include voices from different cultures and communities to provide a well-rounded understanding of the challenges and potential solutions.
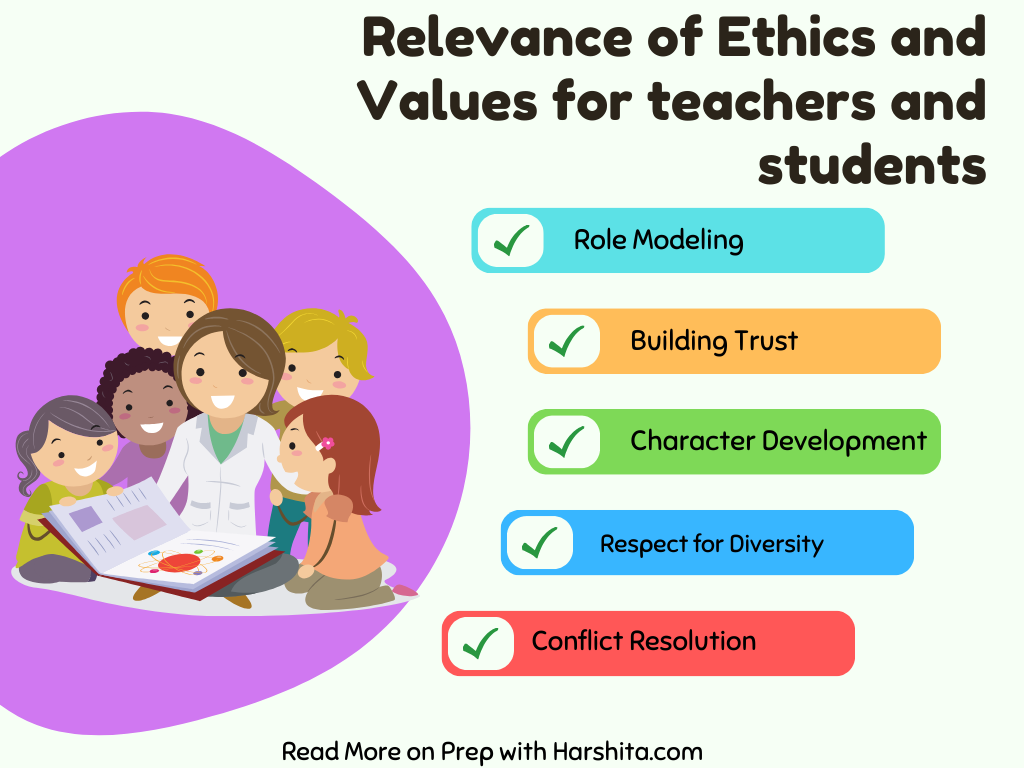
Ethics and Values Education:
Integrate discussions on ethical considerations related to environmental practices and global peace. Encourage students to think critically about values and ethics.
Partnerships with NGOs and Environmental Organizations:
Collaborate with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and environmental organizations to provide students with opportunities for hands-on experiences, field trips, and exposure to real-world initiatives.
Teacher Professional Development:
Provide ongoing professional development for teachers to keep them informed about current global peace and environmental issues. This ensures that educators are equipped to facilitate meaningful discussions and activities in the classroom.
Technology Integration:
Use technology to connect students with global issues. Virtual conferences, online resources, and collaborative projects with students from other parts of the world can help broaden their perspectives.
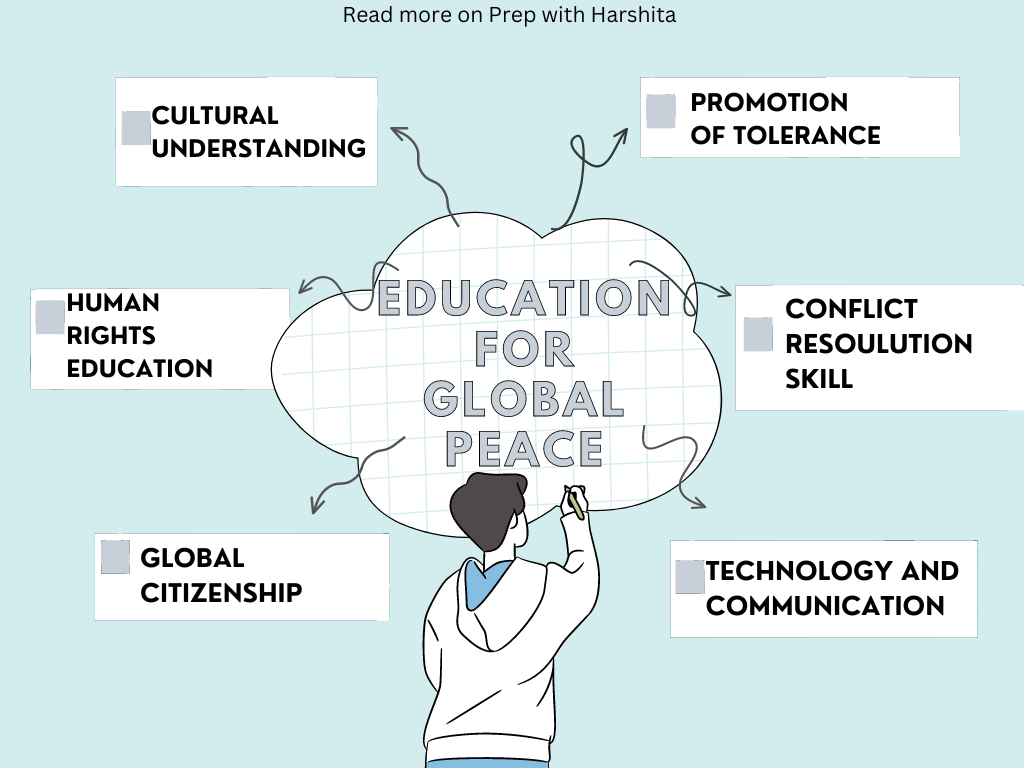
Also Read: Education for Sustainable Development
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita