Academic discipline and school subjects are related concepts in education, but they have distinct meanings and functions. Understanding their differences and relationships is essential for educators, students, and those involved in curriculum development.
Let’s try to understand it in a better way :
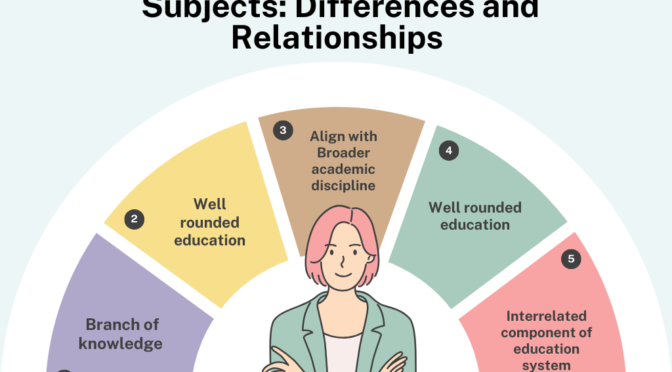
Academic Discipline
An academic discipline refers to a branch of knowledge that is studied at the higher education level, typically in universities and colleges. It includes a specific field of study, often characterized by theories, methodologies, and research practices.
Examples: Physics, sociology, biology, philosophy, psychology, and economics are examples of academic disciplines.
School Subjects
School subjects refer to the specific topics or areas of study taught at the primary and secondary school levels. These subjects are part of the broader curriculum designed to provide a well-rounded education to students.
Examples: Mathematics, English, science, history, geography, and physical education are examples of school subjects.
Differences:
- Academic disciplines are typically studied at the higher education level, while school subjects are taught at the primary and secondary school levels.
- Academic disciplines often involve a higher degree of specialization and depth of knowledge, focusing on advanced theories and research. School subjects are more generalized and aim to provide a broad foundation in various areas of knowledge.
- Academic disciplines are designed to prepare students for in-depth exploration and research within a specific field. School subjects, on the other hand, aim to provide a well-rounded education and develop a range of skills and knowledge applicable to various aspects of life.
Relationship:
- School subjects lay the groundwork for the development of academic disciplines. For example, elementary and high school science classes introduce students to the basics of biology, chemistry, and physics, setting the stage for more specialized study in these disciplines at the university level.
- School subjects offer huge knowledge, exposing students to various disciplines. As students progress in their education, they may choose to go deeper into specific academic disciplines based on their interests and career goals.
- The curriculum at the school level is often designed to align with broader academic disciplines. For instance, the study of history as a school subject may align with the academic discipline of history at the higher education level.
Also Read: Need and Importance of School Subjects
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita