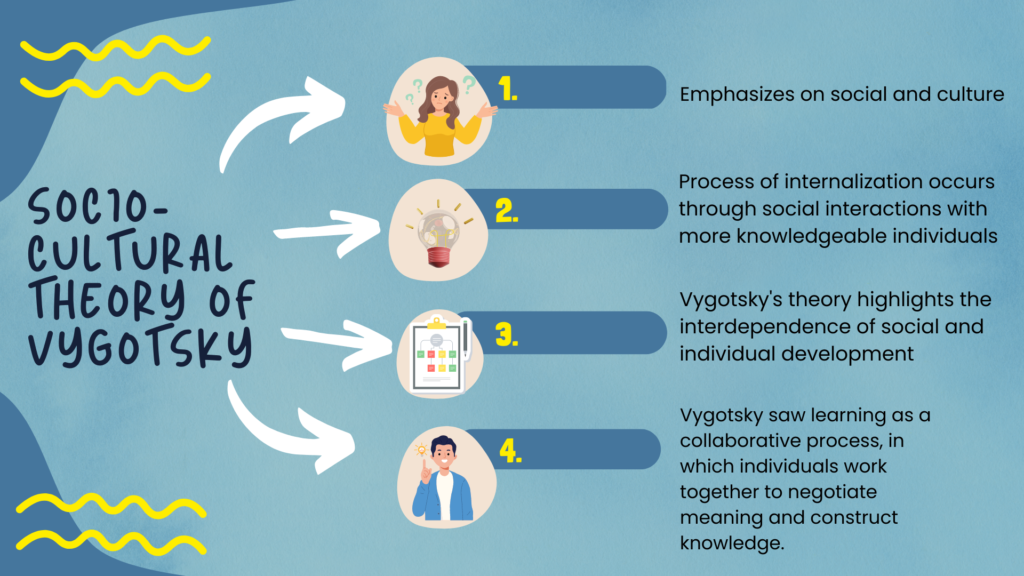
Socio-cultural theory of Vygotsky emphasizes the important role that culture and social interactions play in the development of cognitive abilities. According to Vygotsky, human development occurs through a process of internalizing cultural tools and practices, such as language and symbols, which allow individuals to think and reason at higher levels. This process of internalization occurs through social interactions with more knowledgeable individuals and is facilitated through the use of mediational tools, such as language, which serve to bridge the gap between an individual’s current level of development and their potential for future development. In this way, Vygotsky’s theory highlights the interdependence of social and individual development, and the importance of cultural and historical context in shaping cognitive abilities.
Features of Socio Cultural theory of Vygotsky
- Zone of Proximal Development: The difference between what a child can do independently and what they can do with help from others. This concept highlights the importance of social interaction and guidance in cognitive development.
- Scaffolding: The support and guidance provided by more knowledgeable individuals during the learning process, which helps a child progress to the next level of development.
- Internalization: The process of taking external cultural tools, such as language, and making them one’s own, thereby transforming them into internal mental processes.
- Social Interaction: Vygotsky believed that social interaction is crucial for cognitive development, as individuals learn through their interactions with others.
- Cultural Historical Context: Vygotsky emphasized that cognitive development is shaped by the historical and cultural context in which individuals live.
- Mediation: The use of cultural tools and practices, such as language, symbols, and artifacts, to mediate and transform cognitive processes.
- Collaborative Learning: Vygotsky saw learning as a collaborative process, in which individuals work together to negotiate meaning and construct knowledge.
Also Visit : Difference between Growth and Development
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita