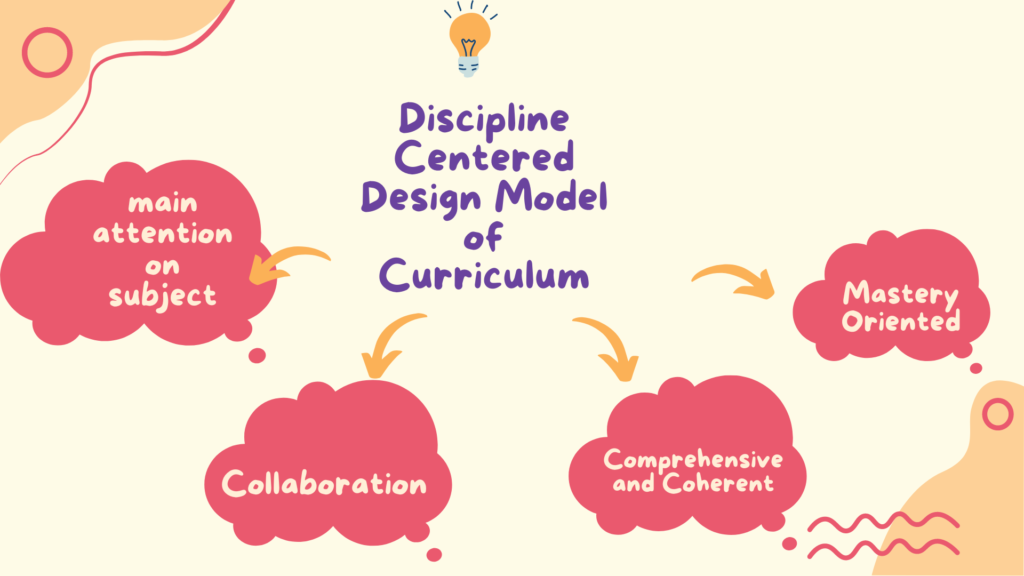
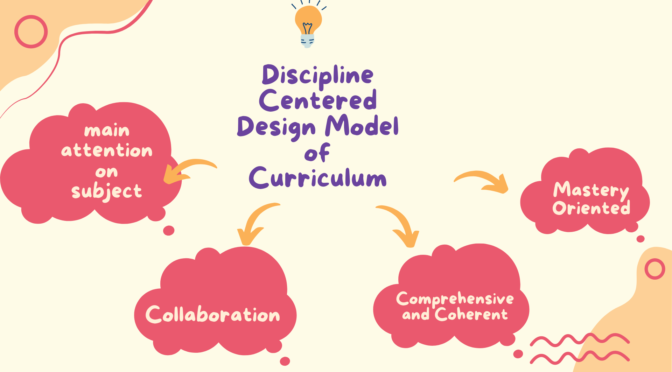
Disciplined-centered Design (DCD) is a model of curriculum design that prioritizes or give major attention to the disciplines or subjects being taught, as the main structure for the curriculum. The DCD model views each discipline as having its own unique body of knowledge, skills, and ways of thinking, and it aims to ensure that students receive a comprehensive and structured education within each discipline. The curriculum is designed around the essential knowledge, skills, and ways of thinking that define each discipline, and it aims to help students build mastery in these areas over time. The DCD model can be useful for ensuring that students receive effective education and that they are able to apply their knowledge and skills across different disciplines.
Few features of Discipline Centered Design :
- Discipline-focused: The DCD model prioritizes the disciplines or subjects being taught as the central structure for the curriculum.
- Coherence: Coherence is a state and situation in which all the parts or ideas fit together well so that they form a united whole The curriculum is designed to ensure coherence within each discipline, so that students receive an integrated education.
- Essential knowledge and skills: The curriculum focuses on the essential knowledge, skills, and ways of thinking that define each discipline.
- Mastery: The curriculum is designed to help students build mastery in each discipline over time.
- Integration with real-world applications: The DCD model may incorporate real-world applications and experiences to help students see the relevance of what they are learning and how they can apply it in the world outside of school.
- Assessment: This model typically includes ongoing assessment to measure student progress and ensure that they are meeting the goals of the curriculum.
- Collaboration: This model may involve collaboration between teachers, subject experts, and other stakeholders to ensure the design and implementation of the curriculum is high-quality and effective.