Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who is famous for his theory of cognitive development, which provides a framework for understanding how children learn and develop their cognitive abilities. According to Piaget’s theory, children progress through four distinct stages of cognitive development, each characterized by different ways of thinking and reasoning.
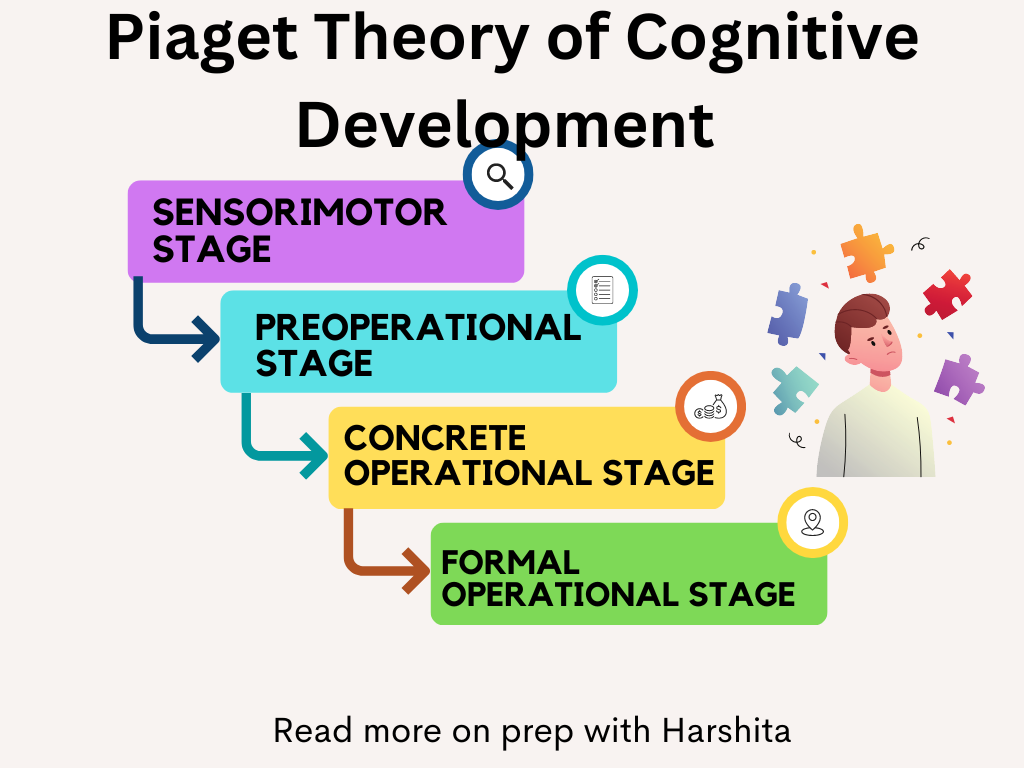
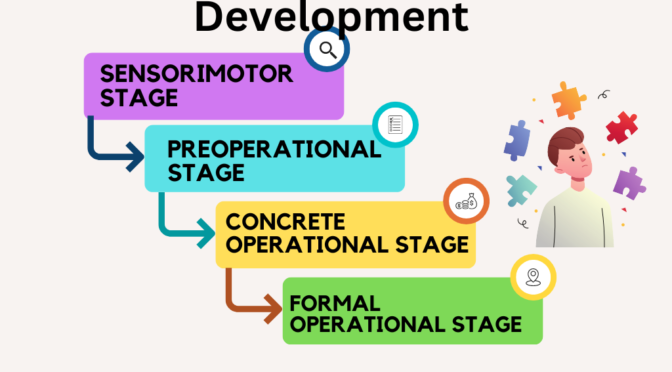
The four stages of Piaget’s cognitive development theory are:
- Sensorimotor Stage: This stage occurs from birth to around two years old. During this stage, infants learn about the world through their senses and motor actions. They develop object permanence, the understanding that an object exists even if it is not currently visible. They also begin to understand cause and effect.
- Preoperational Stage: This stage occurs from around two to seven years old. During this stage, children develop language and the ability to use symbols to represent objects and ideas. They also begin to engage in pretend play and develop a sense of egocentrism, which means they have difficulty understanding that other people may have different perspectives from their own.
- Concrete Operational Stage: This stage occurs from around seven to twelve years old. During this stage, children become more logical and can perform mental operations on concrete objects. They develop the ability to classify objects, understand conservation (that the amount of a substance remains the same even if its appearance changes), and understand reversibility (that a process can be undone).
- Formal Operational Stage: This stage occurs from around twelve years old and continues through adulthood. During this stage, individuals develop the ability to think abstractly, engage in hypothetical reasoning, and use deductive reasoning. They can solve complex problems and understand hypothetical situations.
Piaget’s theory emphasizes the importance of experience in cognitive development. According to his theory, children actively construct their understanding of the world through their experiences, rather than passively receiving information. Piaget also believed that children progress through these stages in a fixed order and cannot skip stages or regress to earlier ones.
Piaget’s theory has been influential in many fields, including education and psychology. However, it has also been criticized for oversimplifying the complexity of cognitive development and for not fully accounting for the role of culture and social influences. Nonetheless, his work has been the foundation of many subsequent theories and has contributed greatly to our understanding of how children learn and develop their cognitive abilities.