Hilda Taba (1902-1967) was an Estonian-American educator and curriculum theorist who is best known for her development of a teaching model called the “Taba Model”.
Features and Steps of the Taba Model:
The Taba Model is a curriculum development model that emphasizes a cyclical process of curriculum development. It is based on student learning needs and experiences.
The Taba Model consists of the following steps:
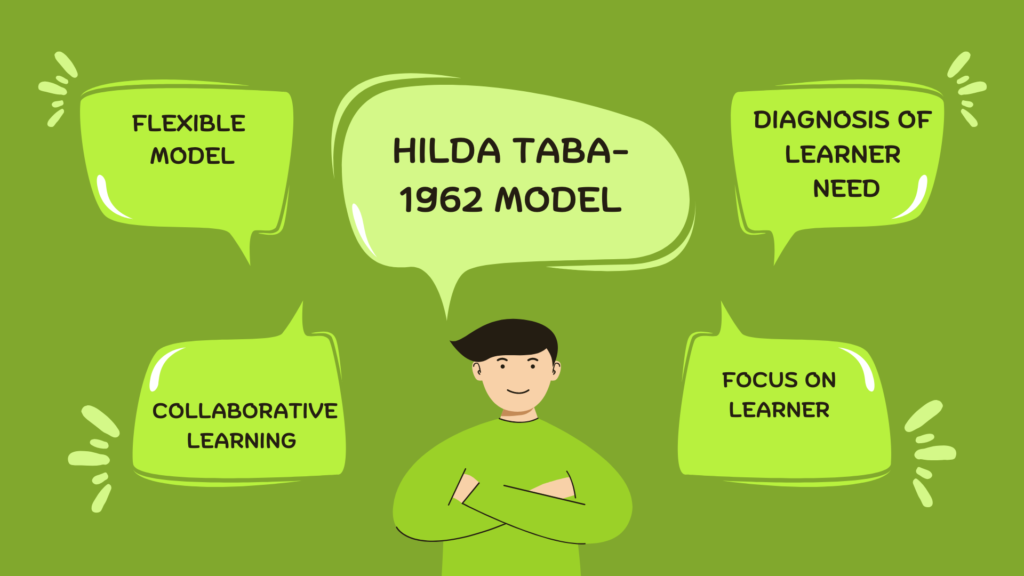
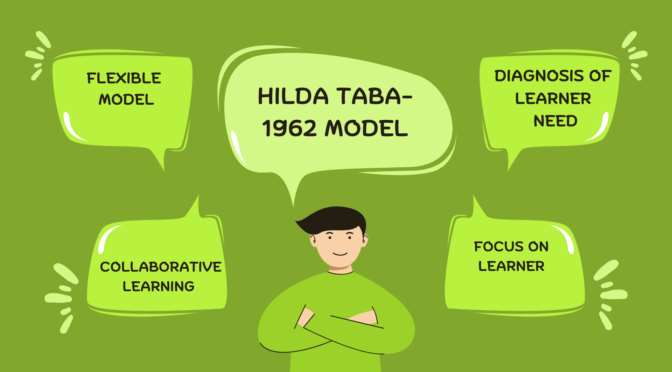
- Diagnosis of learner needs: This step involves identifying the learning needs, interests, and experiences of the students.
- Formulation of objectives: Based on the diagnosis, objectives are formulated that are specific, measurable, and achievable.
- Selection of content: The next step involves selecting content that is relevant to the objectives and the learning needs of the students.
- Organization of content: The selected content is organized into a meaningful and logical sequence.
- Selection of learning experiences: This step involves selecting appropriate learning experiences that will enable students to achieve the objectives.
- Organization of learning experiences: The selected learning experiences are organized into a sequence that help students to achieve the objectives.
- Evaluation: The final step involves evaluating the effectiveness of the curriculum in achieving the objectives.
Features of Hilda Taba Model :
- Focus on learner-centeredness: The Taba Model places a strong emphasis on the learner and their individual needs and interests. The curriculum is relevant and meaningful to the students, and it takes into account their prior knowledge and experiences.
- Spiral approach: The Taba Model uses a spiral approach, where the curriculum is organized around key concepts and ideas that are revisited and deepened over time. This allows students to build on their prior knowledge and make connections between different topics and subjects.
- Critical thinking: This emphasizes the development of critical thinking skills, encouraging students to question, analyze, and evaluate information and ideas.
- Interdisciplinary approach: The Taba Model encourages an interdisciplinary approach to learning, where students can explore connections between different subjects and topics.
- Collaborative learning: The Taba Model promotes collaborative learning, where students work together in groups to explore and solve problems. This helps to develop communication and teamwork skills, as well as foster a sense of community and shared responsibility.
- Flexibility: The Taba Model is designed to be flexible, allowing teachers to adapt the curriculum to meet the needs and interests of their students. So curriculum can be adjusted to accommodate changes in the classroom or new developments in the subject area.
Also Read: Foundation of Curriculum
The Taba Model emphasizes the importance of considering the needs and experiences of the students in the curriculum development process. It is a flexible and adaptable model that can be used in a variety of educational settings.