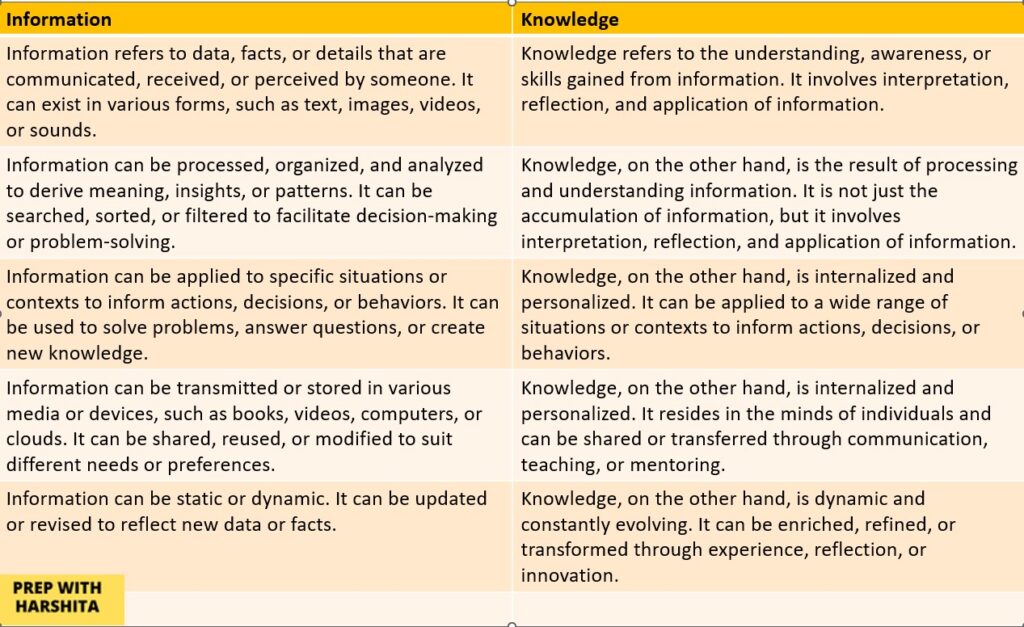
Here are five major differences between information and knowledge:
- Nature: Information refers to data, facts, or details that are communicated, received, or perceived by someone. It can exist in various forms, such as text, images, videos, or sounds. Knowledge, on the other hand, refers to the understanding, awareness, or skills gained from the information. It involves interpretation, reflection, and application of information.
- Processing: Information can be processed, organized, and analyzed to derive meaning, insights, or patterns. It can be searched, sorted, or filtered to facilitate decision-making or problem-solving. Knowledge, on the other hand, is the result of processing and understanding information. It is not just the accumulation of information, but it involves interpretation, reflection, and application of information.
- Application: Information can be applied to specific situations or contexts to inform actions, decisions, or behaviors. It can be used to solve problems, answer questions, or create new knowledge. Knowledge, on the other hand, is internalized and personalized. It can be applied to a wide range of situations or contexts to inform actions, decisions, or behaviors.
- Storage: Information can be transmitted or stored in various media or devices, such as books, videos, computers, or clouds. It can be shared, reused, or modified to suit different needs or preferences. Knowledge, on the other hand, is internalized and personalized. It resides in the minds of individuals and can be shared or transferred through communication, teaching, or mentoring.
- Evolution: Information can be static or dynamic. It can be updated or revised to reflect new data or facts. Knowledge, on the other hand, is dynamic and constantly evolving. It can be enriched, refined, or transformed through experience, reflection, or innovation. Knowledge is not just a static product, it is a process of learning and discovery.
Also Read: Textual and Contextual Knowledge