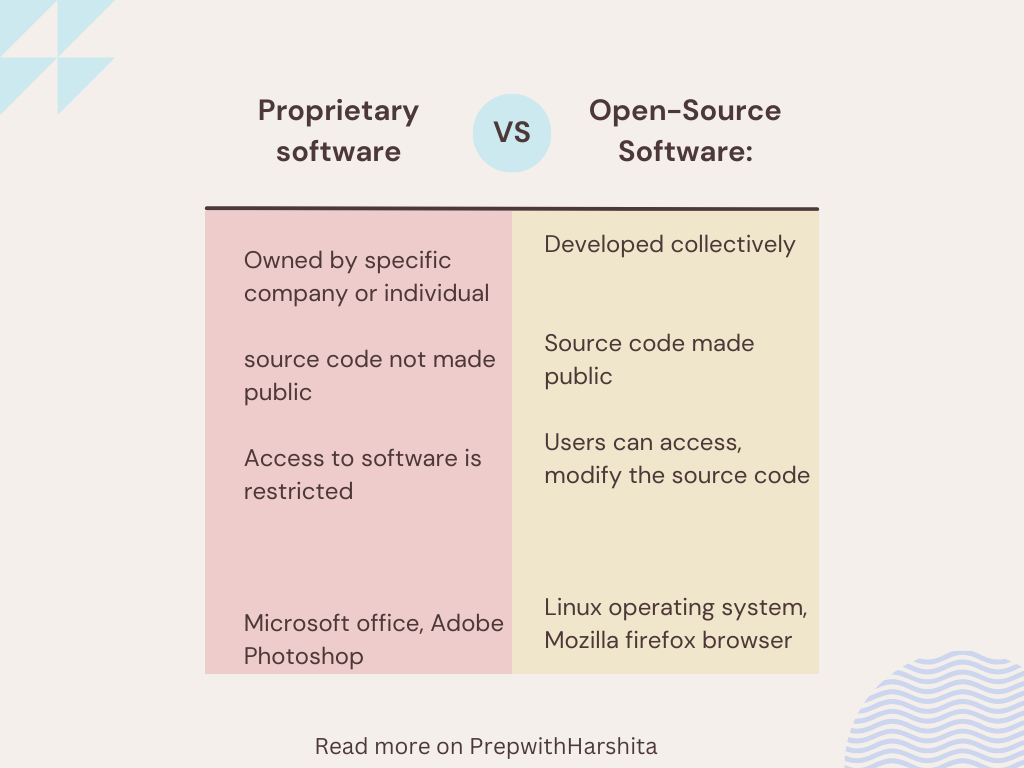
Professional development for teachers is an ongoing and intentional process designed to enhance educators’ knowledge, skills, and effectiveness in the classroom. It is a crucial aspect of the education system, aiming to keep teachers abreast of advancements in pedagogy, curriculum, technology, and educational research. The primary goal of teacher professional development is to improve student learning outcomes by fostering continuous growth and improvement among educators.
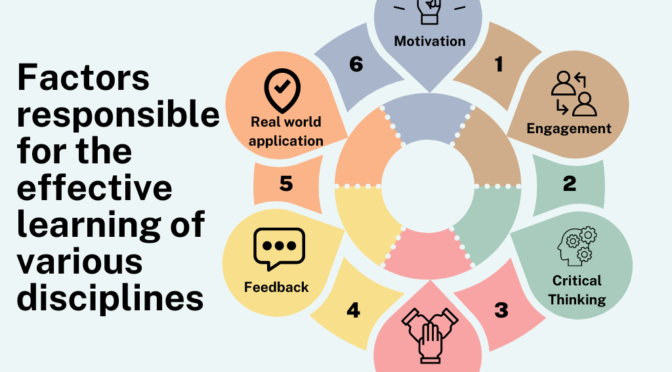
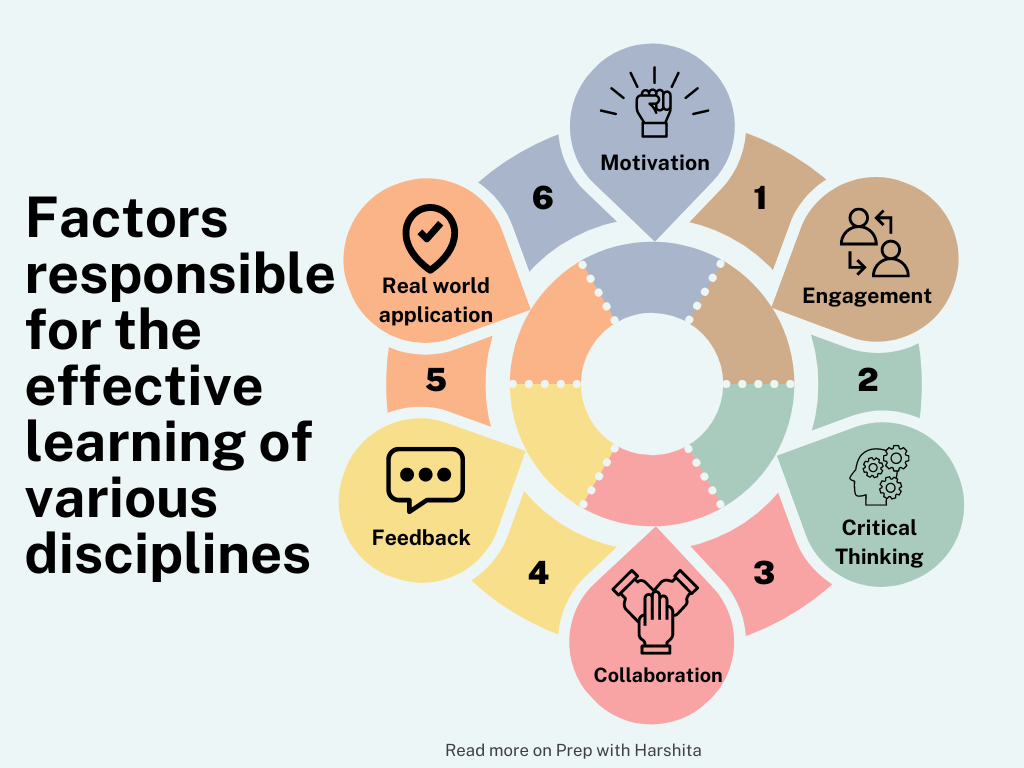
Main Features of Teacher Professional Development :
Lifelong Learning:
Professional development emphasizes the idea of lifelong learning for teachers. It recognizes that education is an evolving field, and educators need to adapt to new methodologies, technologies, and educational theories.
Skill Enhancement:
Teachers engage in this to enhance their teaching skills. This includes altering the instructional techniques, including innovative teaching methods, and staying updated on best practices.
Technology Integration:
Given the rapid advancements in technology, It helps teachers integrate relevant technological tools into their teaching practices. This includes using educational software, online resources, and interactive technologies in the classroom.
Specialization and Certification:
It allows teachers to pursue specialization in specific areas of education or obtain additional certifications. This can enhance their expertise and open up new opportunities within the education field.
Adapting to Educational Trends:
As educational trends evolve, it helps teachers stay informed about changes in educational policies, standards, and methodologies. This adaptability is essential for effective teaching in a dynamic educational landscape.
Also Visit : Concept of Leadership
Forms of Professional Development:
Workshops and Seminars: Short-term, focused sessions that provide targeted training on specific topics.
Online Courses and Webinars: Virtual platforms that offer flexibility for teachers to engage in professional development at their own pace.
In-Service Training: Training sessions provided within the school or district, often tailored to address specific needs or initiatives.
Conferences: Larger gatherings where educators can attend keynote presentations, workshops, and networking events to stay updated on the latest educational developments.
Mentorship Programs: Pairing experienced teachers with newer educators to provide guidance, support, and professional development opportunities.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita