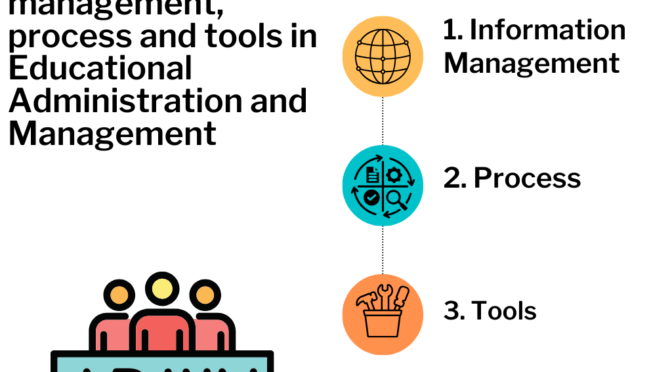
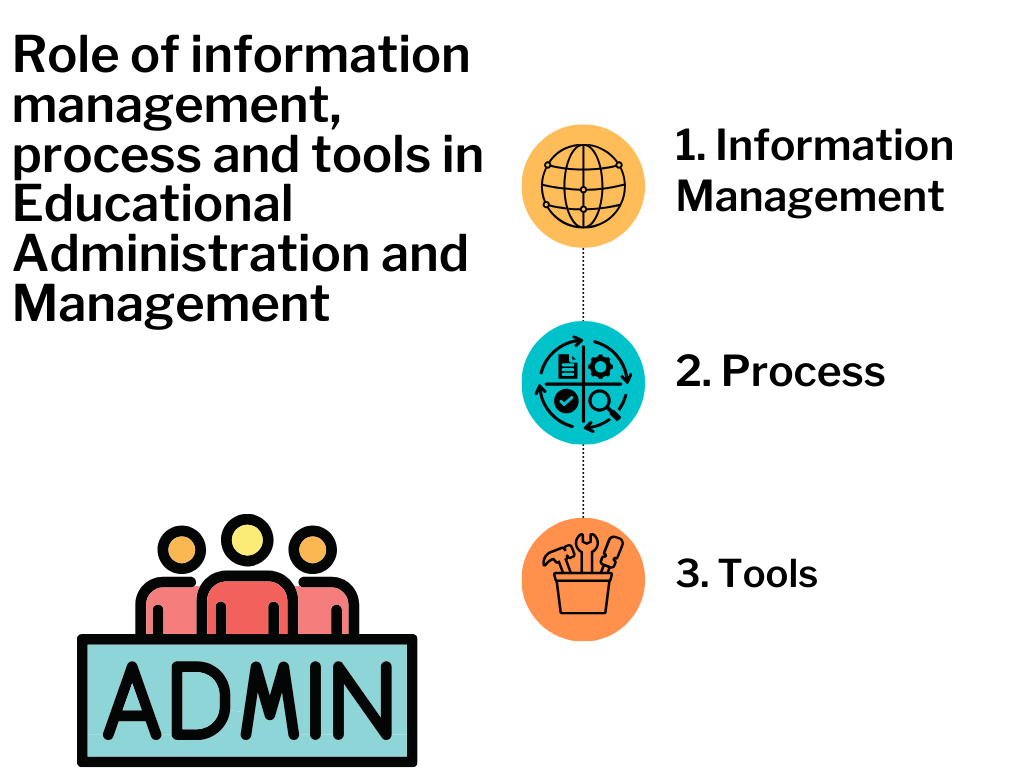
Role of information management process and tools in Educational Administration and Management is very important. Efficient handling of information is essential for the smooth functioning of educational institutions, and the use of appropriate processes and tools can enhance administrative capabilities.
Here’s a breakdown of their roles:
Information Management:
Data collection and Analysis
Educational administrators need accurate and timely data to make informed decisions. Information management ensures efficient collection, storage, and analysis of data related to student performance, attendance, and other relevant metrics.
Strategic Planning
Educational institutions use information to develop plans and policies. Proper management of information allows administrators to identify trends, set goals, and make decisions that align with the institution’s long-term objectives.
Resource Allocation
Information management helps in allocating resources effectively. It enables administrators to identify areas that need additional resources, budgeting, and ensure that resources are allocated based on the institution’s priorities.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of educational programs and processes are important for improvement. Information management helps in the tracking of outcomes, performance metrics, and the effectiveness of various initiatives.
Communication
Effective communication within and outside the institution is vital. Information management ensures that accurate and timely information is shared among administrators, faculty, students, and other stakeholders.
Process:
Workflow Optimization
Smooth working of administrative processes improves efficiency. Properly designed processes help in minimizing errors, and ensuring that tasks are completed in a timely manner.
Decision-Making Processes:
Clearly defined processes helps in decision-making. Administrators can follow established protocols, which promotes consistency.
Policy Implementation:
Processes are essential for implementing policies effectively. They guide administrators in executing policies consistently across the institution.
Quality Assurance:
Processes contribute to quality assurance by setting standards and benchmarks. They provide a base for evaluating and improving the quality of education and administrative services.
Tools :
Data Management Systems:
Implementing proper data management systems facilitates the storage, retrieval, and analysis of large volumes of information, supporting informed decision-making.
Learning Management Systems( LMS):
LMS tools assist in managing educational content, assessments, and communication between students and faculty. They contribute to a more organized and efficient educational process.
Project Management Tools:
Educational projects, such as curriculum development or infrastructure upgrades, benefit from project management tools that facilitate planning, coordination, and tracking of progress.
Communication Tools :
Tools such as email, messaging apps, and collaboration platforms enhance communication among administrators, faculty, and students.
Also Read : Appropriate software Tools for Evaluation
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita (Youtube)