Existentialism is a philosophical and literary movement that emerged in Europe in the 20th century, particularly after World War II. It emphasizes individual freedom, authenticity, and choice.
At the heart of existentialism is the belief that individuals must create their own meaning and purpose in life, rather than relying on external factors such as religion or society. Existentialism emphasizes the importance of personal responsibility, as individuals are responsible for their own choices and actions.
Also read: Pragmatism
Some key themes in existentialism include:
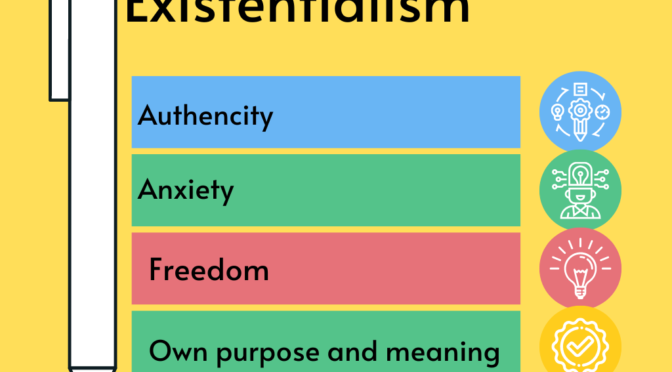
- Authenticity: It stresses the importance of being true to oneself and one’s own values, rather than conforming to external expectations or societal norms.
- Freedom: Existentialism emphasizes the individual’s freedom to make choices and create their own path in life, even in the face of difficult or challenging circumstances.
- Anxiety: It recognizes that the freedom to make choices can also lead to anxiety and uncertainty, as individuals must take responsibility for their own lives and accept the consequences of their choices.
- Existential angst: The existentialist perspective often involves a sense of alienation or isolation from the world and a sense of despair or anxiety about the human condition.
- Existential crisis: It recognizes that individuals may experience a crisis of meaning or purpose, and must confront the question of whether life has any inherent meaning or value.
Overall, existentialism is a complex and multifaceted philosophy that emphasizes individual freedom, responsibility, and the creation of one’s own meaning and purpose in life. It has had a significant influence on literature, psychology, and other fields.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita