There are numerous factors that can affect growth and development like Genetics and environment.
A few of them are mentioned below:
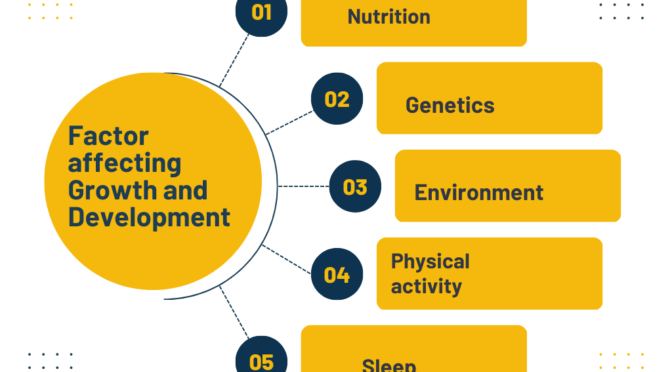
- Genetics: Hereditary factors can determine physical characteristics and predispositions to certain health conditions.
- Environment: The physical, social, and cultural environment in which a person grows up can have a significant impact on their development.
- Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is crucial for healthy growth and development, as it provides the necessary nutrients for the body to grow and function properly.
- Hormones: Hormones play a critical role in growth and development, including puberty and reproductive development.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise and physical activity can help promote healthy growth and development, as well as overall health and well-being.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is important for growth and development, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate tissues.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as chronic illnesses, infections, or injuries, can affect growth and development.
- Parental factors: Parental behavior, including parenting style, discipline, and involvement, can have a significant impact on a child’s development.
- Socioeconomic status: Socioeconomic status can affect access to resources, such as education and healthcare, that can impact growth and development.
- Cultural factors: Cultural beliefs and values can influence growth and development, particularly in terms of socialization and identity formation.
Growth refers to the physical changes that occur in a child’s body, such as increases in height, weight, and the size of organs and bones.
Development, on the other hand, refers to the broader changes in a child’s cognitive, emotional, social, and behavioral skills and abilities.
Factors affecting growth and development are including genetics, nutrition, physical activity, environment, and social and emotional experiences.
Also read: Parenting Styles