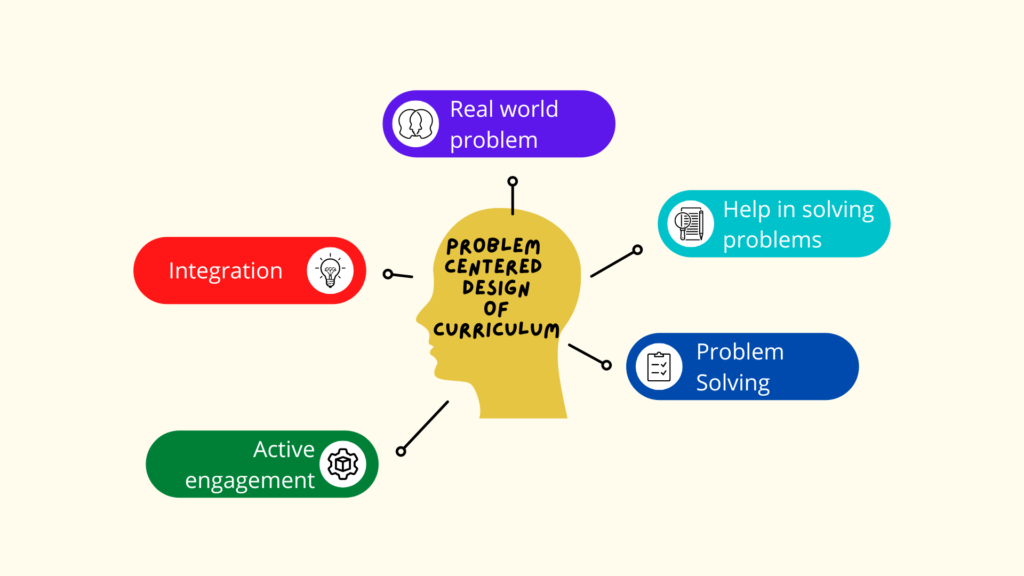
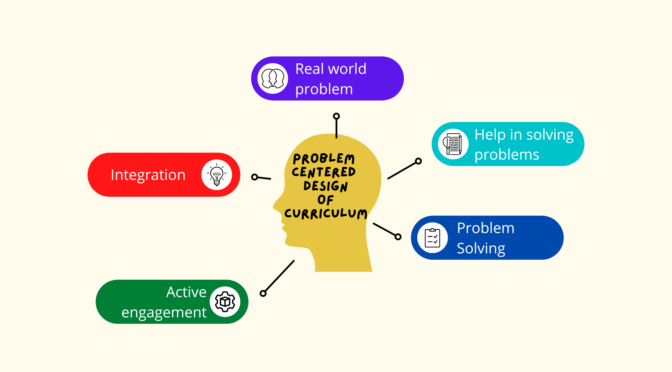
Problem-centered design of curriculum is an educational approach that focuses on addressing real-world problems and challenges as the center of the learning experience. This design is focused on students and help in solving problems that are relevant to lives of student and that connect to their personal interests and future goals. The curriculum is designed to be relevant, engaging, and meaningful, and it provides opportunities for students to use their knowledge and skills to tackle real-world problems. The teacher not act as a leader but as a facilitator and provides support, guidance, and feedback as students so they can work through the problem-solving process. This approach is believed to lead to deeper and meaningful learning and increased motivation and engagement for students, as they are able to learn the practical applications of what they are learning.
The main features of a problem-centered design of curriculum include:
- Relevance: The curriculum is designed to address real-world problems that are relevant to students’ lives and interests.
- Problem-solving: Students are actively engaged in solving problems, using their knowledge and skills to develop solutions.
- Authenticity: The problems addressed in the curriculum are genuine and reflect the challenges faced in real life.
- Collaboration: Students work together to solve problems, encouraging teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills.
- Active engagement: The curriculum provides opportunities for hands-on, experiential learning that keeps students engaged and motivated.
- Integration of content areas: The curriculum integrates multiple content areas, allowing students to see the interconnectedness of different subjects.
- Real-world applications: The curriculum provides opportunities for students to apply what they have learned to real-world situations.
- Teacher as facilitator: The teacher plays a supportive role, helping students to explore and make sense of the problem-solving process, rather than delivering information.