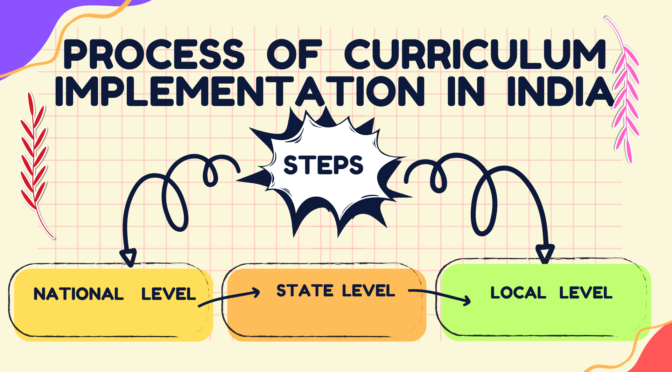
In India, curriculum implementation is carried out at different levels of the education system, including the national, state, and local levels.
Few points to consider:
- The Ministry of Education, formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development, is responsible for developing and implementing national education policies, guidelines, and curricula for various levels of education, from primary to higher education.
- The National Curriculum Framework (NCF), developed by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), provides guidelines for the development of curricula and textbooks for schools in India. The NCF emphasizes the development of a learner-centered and holistic approach to education, with a focus on promoting critical thinking, creativity, and social and emotional learning.
- At the state level, each state has its own education board, which is responsible for developing and implementing state-level curricula and policies, based on the national guidelines. The state-level curricula are aligned with the national curriculum, but may also include state-specific subjects or topics.
- Curriculum implementation in India also involves the selection and training of teachers, the development of teaching materials and resources, and the assessment of learning outcomes. In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on using technology to support curriculum implementation, such as the use of digital learning platforms and online resources.
The steps of curriculum implementation in India may vary depending on the level of education and the specific curriculum being implemented, but generally, the following steps are involved:
- Planning: The first step in curriculum implementation is planning, which involves setting objectives, developing a timeline, identifying resources needed, and allocating responsibilities to different stakeholders.
- Teacher training: Teachers play a critical role in curriculum implementation, and thus, they need to be trained on the new curriculum and instructional methods. This may involve workshops, training sessions, or peer coaching.
- Resource development: Curriculum implementation requires the development of teaching and learning materials, such as textbooks, lesson plans, multimedia resources, and assessment tools. These resources should be aligned with the curriculum objectives and the needs of the learners.
- Implementation: Once the curriculum, resources, and teachers are prepared, the curriculum can be implemented in the classroom. This involves delivering instruction, facilitating student learning, and assessing student progress.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Curriculum implementation should be monitored and evaluated to determine its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This may involve conducting formative assessments, observing classroom instruction, and collecting feedback from teachers, students, and parents.
- Revision and improvement: Based on the results of the monitoring and evaluation process, the curriculum may need to be revised or improved to address any weaknesses or gaps. This may involve making adjustments to the curriculum objectives, content, or instructional methods.
- Scaling up: If the curriculum is found to be effective, it can be scaled up to reach a larger number of schools and learners. This may involve providing additional training to teachers, developing more resources, and expanding infrastructure and support systems.
Challenges in Curriculum Implementation in India:
Despite these efforts, there are still several challenges in curriculum implementation in India, such as
- Inadequate infrastructure,
- limited resources, and a
- lack of teacher training and support
There is a need for greater alignment between the curriculum and the job market, to ensure that learners are prepared for the changing needs of the economy.
Also Read : Factor influencing Curriculum Change
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita