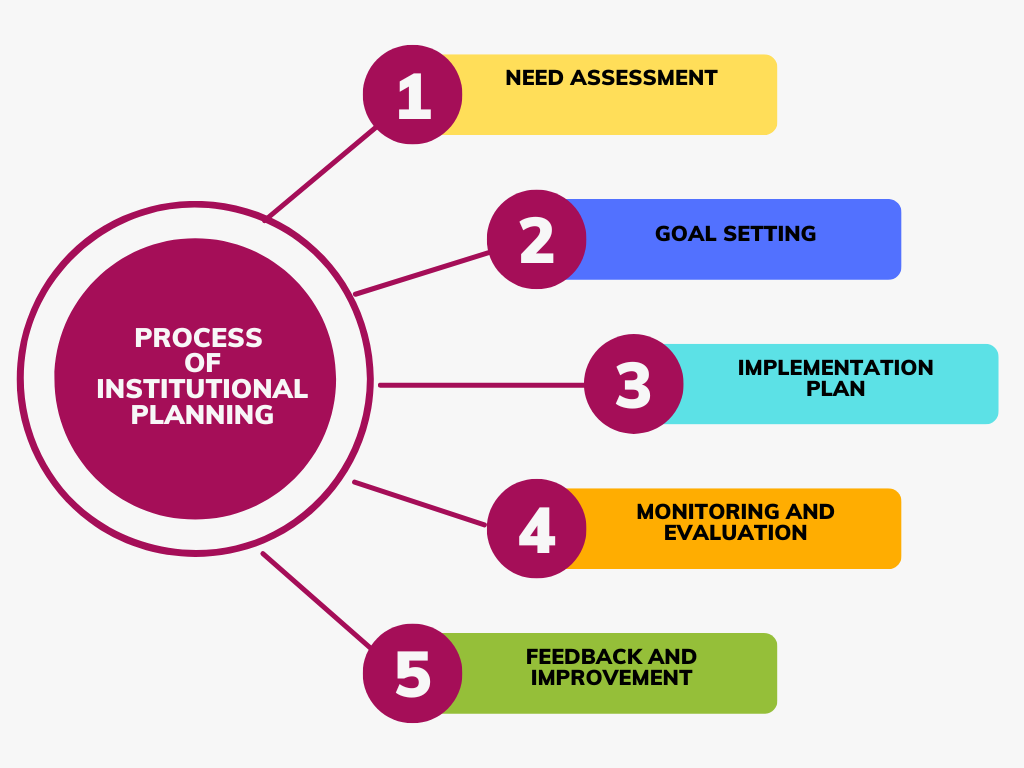
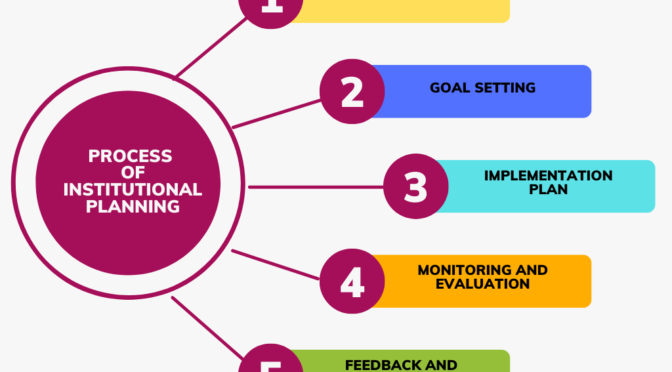
The process of institutional planning in India involves several steps and stages. Here is a general overview:
- Needs Assessment: This is the first stage in the planning process, where the institutions identify the needs and gaps in their existing resources, infrastructure, and manpower. It also involves identifying the needs of the stakeholders such as students, faculty, and the community.
- Goal Setting: Once the needs are identified, the institution sets goals and objectives to meet those needs. These goals must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Resource Mobilization: The institution then identifies the resources required to achieve its goals and objectives. This includes financial resources, human resources, infrastructure, and technology.
- Implementation Plan: The institution then develops an implementation plan, which outlines the specific steps, activities, and timelines required to achieve its goals and objectives. This plan must be comprehensive and include details on budget, human resources, infrastructure, and technology.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: This stage involves continuous monitoring and evaluation of the implementation plan to ensure that the goals and objectives are being met. This includes regular review of progress, assessment of outcomes, and identification of any issues or challenges.
- Feedback and Improvement: Based on the results of the monitoring and evaluation, the institution makes necessary changes and improvements to its implementation plan to ensure that it is effective in achieving its goals and objectives.
Overall, the process of institutional planning in India is a dynamic and ongoing process, which requires continuous review and improvement to ensure that institutions are meeting the needs of their stakeholders and contributing to the overall economic development of the country.