India has made significant contributions to open-source software and the sharing of digital content. Here are some notable Indian initiatives in open-source software and sharing of digital content:
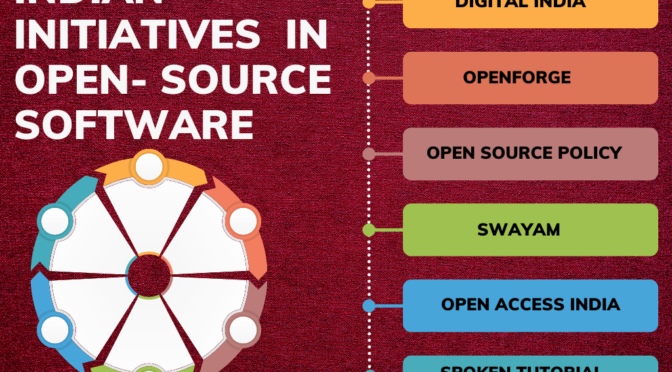
Digital India
Launched by the Government of India, Digital India aims to transform the country into a digitally empowered society.
Digital India encourages the use of open-source software to ensure accessibility, affordability, and security in the digital space.
OpenForge:
An initiative by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), OpenForge is a collaborative platform for hosting and sharing of e-governance applications and open-source projects.
It facilitates the development of e-governance applications using open-source technologies, fostering transparency and innovation.
Open Source Policy:
The Indian government has actively embraced open-source policies, emphasizing the use of open-source software in various departments.
By adopting open-source solutions, the government aims to reduce costs and promote the development of locally customizable software.
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds):
SWAYAM is an initiative by the Ministry of Education that provides online courses for students.
Content on SWAYAM is often released under open licenses, allowing for the sharing and reuse of educational resources.
Open Access India:
Open Access India is an advocacy group promoting open access, open data, and open education.
The group collaborates with various stakeholders, including researchers, institutions, and policymakers, to promote openness in research and education.
Spoken Tutorial Project:
Launched by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, the Spoken Tutorial Project focuses on teaching and learning open-source software.
It aims to empower individuals, especially students, with skills in open-source technologies through easy-to-follow video tutorials.
Collaborations with Global Open Source Communities:
Indian developers and organizations actively contribute to global open-source projects.
Collaboration with international open-source communities fosters knowledge exchange and the development of cutting-edge technologies.
Also Read: Refresher Courses for Teacher
India’s initiatives in open-source software and digital content sharing not only promote technological innovation but also contribute to the democratization of information and the empowerment of individuals across the country.

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita